A Simple Remote IoT Device Connect Example For Everyday Use
Have you ever wondered how those clever gadgets in your home or even far-off sensors talk to each other without being plugged directly into your computer? That, my friend, is where a remoteiot device connect example really shines. It's about getting things to communicate over distances, making life a little easier, or perhaps helping businesses keep tabs on important stuff. It's a pretty big deal these days, you know, with more and more devices popping up everywhere.
Think about your smart thermostat, for instance, or maybe a tiny weather station out in the garden. They gather information, and then somehow, that information makes its way to your phone, no matter where you are. This kind of remote chat between devices and a central system, often in the cloud, is what we're going to explore. It's actually quite fascinating how it all comes together, allowing you to manage things from afar.
This article will walk you through what goes into a typical remoteiot device connect example. We'll chat about the different bits and pieces involved, how they link up, and some simple ways to make sure everything works smoothly. You'll get a pretty good idea of what it takes to get your own devices talking, whether for a fun project or something more practical, honestly.
Table of Contents
- What is Remote IoT Connection?
- Why Remote Connection Matters
- The Basic Ingredients for a Remote IoT Device Connect Example
- A Conceptual Remote IoT Device Connect Example
- Keeping Your Remote IoT Secure
- Common Things That Might Go Wrong and How to Fix Them
- Future Thoughts on Remote IoT
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Remote IoT Connection?
Remote IoT connection is simply when a physical object, like a sensor or a machine, sends or receives information over a network without needing someone right there to plug it in or press buttons. It's about things communicating from a distance, usually over the internet. This lets you keep an eye on things, or even control them, from pretty much anywhere, which is rather handy.
This kind of connection helps gather data from places that are hard to reach or very spread out. Imagine monitoring the temperature in a remote cabin or checking the water levels in a distant farm field. It's all done through these clever remote links, so you don't have to be physically present, you know.
Why Remote Connection Matters
The ability to connect devices remotely opens up a whole bunch of possibilities. For homes, it means smart lighting you can control from your phone, or security cameras that send alerts when you're away. It makes daily life a bit more convenient, and arguably safer, too.
For businesses, it's about efficiency and getting a better picture of what's happening. Companies can track inventory, monitor machinery for potential issues before they become big problems, or even manage entire fleets of vehicles. This can save a lot of money and time, which is something every business likes, obviously. The insights gained from remote data can help make better decisions, leading to improvements across the board, in a way.
It also means new services and products can pop up. Think about health monitors that send data to doctors automatically, or smart city systems that manage traffic lights based on real-time flow. The world is becoming more connected, and remote IoT is a big part of that, at the end of the day. It allows for a constant flow of information that helps systems adapt and respond without human intervention, which is quite powerful.
The Basic Ingredients for a Remote IoT Device Connect Example
To make a remote IoT connection happen, you need a few key pieces working together. It's like baking a cake; you can't just have one ingredient. Each part plays a specific role in getting information from your device to where it needs to go, and then maybe back again, too.
The Device Itself
This is the physical thing that does the sensing or acting. It could be a tiny sensor that measures temperature, a camera, or a motor that opens a gate. It needs to have some way to gather information or perform an action, and it also needs a way to communicate, so.
These devices often have small processors, like tiny brains, and memory to store data temporarily. They are built to be efficient, sometimes running on batteries for a long time. The choice of device really depends on what you want to achieve with your remote IoT setup, you know.
Connectivity Options
This is how your device talks to the outside world. There are many ways for devices to connect, and the best choice often depends on how far the data needs to travel, how much data there is, and how much power the device can use. It's a bit like picking the right road for your journey, actually.
- Wi-Fi: Good for shorter distances, like within a home or office, and when you have a lot of data to send. It uses more power, so devices often need to be plugged in or have larger batteries.
- Cellular (4G/5G): Great for long distances, like devices out in the field or in vehicles. It's reliable and can handle a fair amount of data, but it typically costs money for data plans.
- LoRaWAN/NB-IoT: These are for very low-power devices that send small bits of data over long distances. Think of sensors that only send readings once an hour. They are very energy efficient, which is really good for battery-powered things.
- Satellite: For truly remote locations where no other network is available. It's generally more expensive and slower, but it works almost anywhere on Earth, so that's something.
The Cloud Platform
Once your device sends its data, it usually goes to a cloud platform. This is like a big, secure data center on the internet that collects, stores, and processes all the information from your devices. It's where the magic happens, where raw data turns into something useful, you see.
Cloud platforms offer various services for IoT, like managing your devices, storing their data, and providing tools to analyze that data. They also help secure the connections and make sure only authorized devices can send information. Companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft offer these services, among others, pretty much.
Your Application
This is the part you interact with. It could be a mobile app on your smartphone, a website, or a special software program on your computer. This application takes the processed data from the cloud platform and presents it to you in a way that makes sense. It also lets you send commands back to your devices, like turning a light on or off, you know.
The application is your window into the remote world of your devices. It's how you see what's happening and how you take action. It needs to be user-friendly and clearly show the information you need, so that's important.
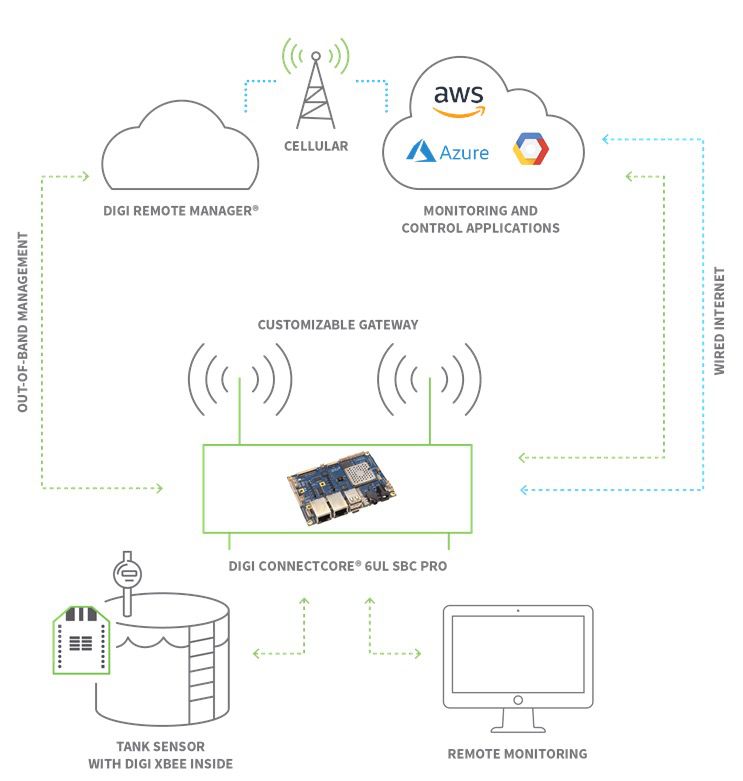
A Conceptual Remote IoT Device Connect Example
Let's imagine a simple scenario: you want to monitor the temperature in your detached garage or shed from your phone, even when you're at work. This is a classic remoteiot device connect example, and it shows how all the pieces fit together. We'll break it down step by step, just a little.
Step 1: Preparing the Device
First, you'd get a small temperature sensor device. This device would have a tiny computer inside, like a micro-controller, and a Wi-Fi chip, since your home Wi-Fi reaches the garage. You'd load some basic instructions onto it, telling it to read the temperature every few minutes, for instance.
These instructions would also tell the device how to connect to your home Wi-Fi network. You'd put in your Wi-Fi name and password, just like you do for your phone. This setup makes the device ready to send its readings out, so it's a bit like getting it dressed for the party.
Step 2: Choosing a Connection Method
For our garage example, Wi-Fi is a good choice because it's available and generally reliable within a home property. If the garage were much further away, or if you didn't have Wi-Fi there, you might consider a cellular connection or even a low-power option like LoRaWAN, you know. The choice really depends on the specific situation and how much data you need to send, actually.
Since Wi-Fi is already there, it means you don't need extra hardware like a cellular modem for the device. This keeps things simpler and usually less expensive for a home setup. It's a pretty common way to get things talking over a short to medium distance, generally.
Step 3: Setting Up the Cloud
Next, you'd pick a cloud platform. For a simple project, something like Google's Firebase or Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Core could work. You'd create an account and set up a specific "project" or "thing" for your temperature sensor within that cloud service.
This involves telling the cloud platform that a new device is going to connect and giving it a unique identity. The cloud platform provides a special address and security keys that your device will use to send its data safely. It's like getting a post office box ready for incoming mail, basically.
Step 4: Securing the Connection
Security is super important. When your device sends temperature data, you want to make sure no one else can snoop on it or pretend to be your device. The cloud platform gives you special digital certificates or keys.
You'd put these keys onto your temperature sensor device. When the device tries to send data, it uses these keys to prove its identity to the cloud, and the cloud uses them to confirm it's talking to the right device. This creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for the data, making it very hard for unauthorized people to get in, which is really good.
Step 5: Making It All Talk
Now, you'd update the instructions on your temperature sensor device. These instructions would tell it to connect to your Wi-Fi, then use those special security keys to connect to the cloud platform. Once connected, it would start sending the temperature readings regularly.
The device uses a specific communication language, often something like MQTT, to send its data. It's a lightweight way for devices to publish information to the cloud, like sending out a tiny tweet with the temperature reading. The cloud platform is always listening for these messages from your device, so that's how it works.
Step 6: Seeing the Data
Finally, you'd create a simple application, maybe a web page or a basic app on your phone. This application would connect to the same cloud platform. It would be set up to "subscribe" to the temperature data coming from your garage sensor.
When the sensor sends a new temperature reading to the cloud, the cloud then pushes that data to your application. Your application then displays the current temperature, perhaps even showing a graph of how it's changed over time. This lets you check your garage temperature from anywhere, which is pretty neat, honestly. Learn more about connecting devices on our site.
Keeping Your Remote IoT Secure
Keeping your remote IoT setup safe is a big deal, really. Just like you wouldn't leave your front door unlocked, you don't want your devices to be easy targets for bad actors. A breach could mean your data is stolen, or worse, someone could take control of your devices, which is a bit scary.
Always use strong, unique passwords for your devices and cloud accounts. It sounds simple, but it's often overlooked. Make sure the connections between your devices and the cloud are encrypted. This scrambles the data so only authorized parties can read it, so it's like sending a secret message in code.
Keep your device software and cloud platform settings up to date. Software updates often include fixes for security holes that bad actors might try to exploit. Regularly check who has access to your cloud account and remove anyone who doesn't need it. It's about being vigilant and proactive, just a little, to keep everything running smoothly and safely. You can find more helpful information about securing your accounts on official help centers, for example.
Common Things That Might Go Wrong and How to Fix Them
Even with a simple remoteiot device connect example, things can sometimes hit a snag. It's part of working with technology, you know. But most problems have straightforward solutions, so don't get too worried.
- Device Not Connecting to Wi-Fi: Double-check your Wi-Fi name and password. Make sure the device is close enough to your Wi-Fi router. Sometimes, just restarting the router helps, too.
- No Data Showing in the Cloud: Check if the device is actually sending data. Look at the device's status lights or logs if it has any. Make sure the security keys or certificates are correctly installed on the device and match what the cloud expects.
- Data Not Showing in Your App: Confirm your app is correctly connected to the cloud platform and is "subscribing" to the right data stream. Sometimes, a simple refresh of the app or web page can fix it.
- Intermittent Connection: This could be a weak Wi-Fi signal or cellular signal. Consider moving the device closer to the signal source or adding a signal booster. It might also be power related, so check the battery or power supply, honestly.
- Device Overheating: Ensure the device has proper ventilation and isn't in direct sunlight. Some devices are sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Patience is key when troubleshooting. Go through each step logically, and often, the solution becomes clear. It's more or less like solving a puzzle, you see.
Future Thoughts on Remote IoT
The world of remote IoT is constantly growing and changing. We're seeing more and more devices, from tiny wearable health trackers to massive industrial machines, all talking to each other from afar. This trend is only going to continue, with more advanced sensors and even smarter ways for devices to connect, which is pretty exciting.
Expect to see even more focus on making these connections super secure and very energy efficient. New communication methods might pop up, making it even easier and cheaper to connect devices in far-flung places. The possibilities are really quite vast, and it's a space that's always evolving, so that's something to look forward to. Perhaps soon, even more devices will simply connect themselves, making setup even simpler, in a way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions people often have about connecting devices remotely, honestly.
How much does it cost to connect an IoT device remotely?
The cost can vary quite a bit, depending on what you're doing. It includes the price of the device itself, which could be anywhere from a few dollars for a simple sensor to hundreds for something more complex. Then there's the cost of connectivity, like a cellular data plan if you use that, or just your existing Wi-Fi. Cloud platform usage can be free for small projects but can go up if you have lots of devices sending tons of data. So, it's not a one-size-fits-all answer, you know, but often quite affordable for personal projects.
Can I connect any device to the internet?
Not every device can just connect to the internet right out of the box. A device needs specific hardware, like a Wi-Fi chip or a cellular modem, and the right software to communicate. Older devices usually don't have this built-in. However, you can often "smartify" older devices by adding an IoT gateway or a smart plug that gives them some remote control capabilities. It's about giving them the right tools to talk, basically.
Is remote IoT device connection safe from hackers?
No system is 100% safe, but remote IoT connections can be made very secure. Using strong encryption, unique device identities, and regularly updating software are key steps. It's also important to use reputable cloud platforms that have good security practices. Thinking about security from the very start, rather than as an afterthought, makes a huge difference. You're always trying to stay a step ahead, like your email security, more or less.
IoT device remote control with FlexiHub
Mastering SSH Access To IoT Devices On Windows 10: The Ultimate Guide

Mastering Secure IoT Connections: A Step-by-Step SSH Guide For Ubuntu