The Best Remote IoT Behind Router Raspberry Pi Free Solutions
Do you ever dream of having your smart devices, perhaps powered by a tiny Raspberry Pi, talking to you from anywhere, even when you're far from home? It's a common wish for many, and getting your Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets to work seamlessly from outside your home network can feel a bit like trying to send a message in a bottle across a vast ocean. Your home router, while keeping your network safe, often acts like a very secure gate, making it tricky for outside connections to reach your little computers inside.
For folks who love to tinker and build their own smart home setups, the idea of having free, reliable access to their Raspberry Pi projects is very appealing. You've put time into creating something cool, and you want to keep an eye on it or even give it commands, no matter where you happen to be. This challenge of connecting to devices tucked away behind your router, without paying for services or opening up your network to risks, is something many people face, so it's a very good question to ask how to do it.
This article will explore some of the best ways to achieve just that – remote access to your Raspberry Pi IoT projects, all without costing you a penny. We'll look at clever methods that let you control your smart devices from afar, keeping things secure and simple. We're going to talk about what was the best choice for this purpose, and how you can make the best of your time setting these things up.
Table of Contents
- Why Remote IoT with Raspberry Pi?
- Unlocking Your Pi: Top Free Remote Access Methods
- Prioritizing Security: Keeping Your IoT Safe
- Getting Started: A Gentle Path
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why Remote IoT with Raspberry Pi?
The Allure of Control
There's something truly satisfying about having your own custom-built smart home setup. Maybe you've got a Raspberry Pi monitoring your plants, or perhaps it's controlling your lights. Being able to check on these things, or even change how they work, from anywhere in the world, adds a lot of convenience, so it's almost like magic. It gives you a sense of freedom and makes your projects feel truly connected.
Think about being on vacation and wanting to make sure your pet feeder dispenses food, or checking if your garage door is closed. With remote access, these actions become very simple. It's about extending the reach of your personal creations, making them useful even when you're not physically present. That's a pretty powerful idea, isn't it?
Overcoming Network Hurdles
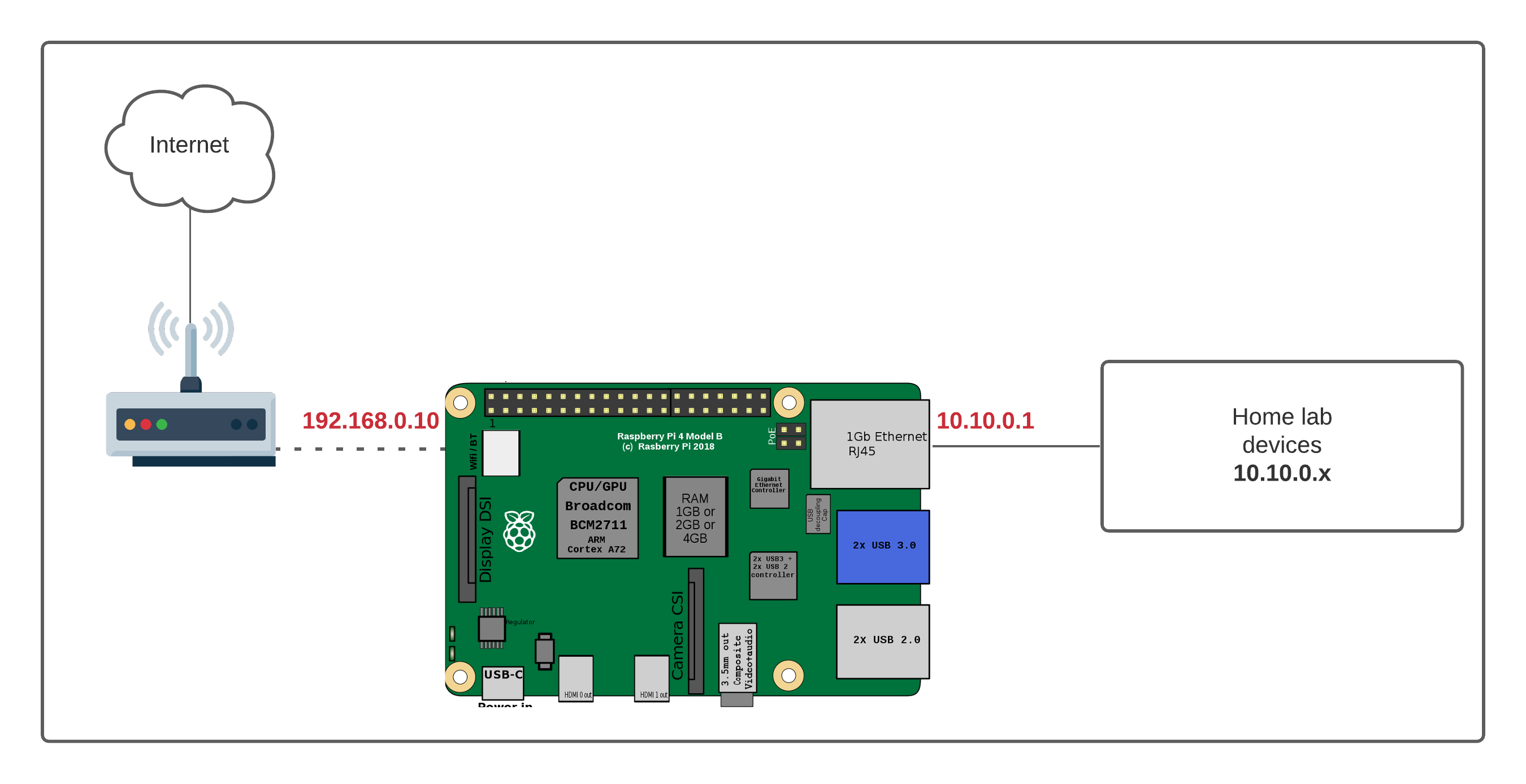
The biggest challenge for most people wanting to access their Raspberry Pi from afar is the home router. Routers are designed to protect your internal network from unwanted visitors, and they do a very good job of it. This means they typically block incoming connections unless you specifically tell them not to, which is called port forwarding, and many folks prefer not to do that for security reasons, or just can't.
This is where the "behind router" part of our discussion becomes important. We need ways to bypass or cleverly work with this protective barrier without making your home network vulnerable. We're looking for solutions that let your Pi reach out to the internet, rather than waiting for the internet to try and reach in, which is a safer approach, arguably.
Unlocking Your Pi: Top Free Remote Access Methods
Finding the best remote IoT behind router Raspberry Pi free options means looking at clever ways your Pi can talk to the outside world without opening up your home network too much. There are several good methods that hobbyists and even professionals use, and they don't cost anything to get going, which is rather nice.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Solutions
Setting up your own VPN server on your Raspberry Pi is one of the most secure and effective ways to get remote access. Think of a VPN as creating a secure tunnel directly into your home network from wherever you are. Once connected through this tunnel, your remote device acts as if it's physically inside your home network, letting you access your Pi and other devices just like you would if you were sitting right there, so it's very useful.
Pros:
- High Security: All traffic through the VPN is encrypted, keeping your data private.
- Full Network Access: You can access any device on your home network, not just the Pi.
- Free to Use: Software like OpenVPN or WireGuard are open source and cost nothing.
Cons:
- Initial Setup: It can be a bit more involved to set up for the first time, requiring some technical comfort.
- Router Configuration: You might need to set up port forwarding on your router for the VPN server itself, which is a slight exception to our "no port forwarding" desire for the IoT devices themselves.
- Dynamic IP Issues: If your home internet service provider gives you a changing IP address, you'll need a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service, which many offer for free.
To get started, you'd typically install OpenVPN or WireGuard on your Raspberry Pi. There are many guides online that walk you through the steps, and they are usually very clear. You then install a client app on your phone or laptop, connect to your home VPN, and boom – you're in, basically. This is one of the best ways to get full, secure access.
SSH Tunneling and Reverse SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a way to securely access your Raspberry Pi's command line. SSH tunneling takes this a step further, allowing you to forward network traffic through that secure connection. Reverse SSH is particularly clever for behind-router scenarios. Instead of you connecting in, your Raspberry Pi makes an outgoing connection to a public server you control (even a cheap cloud VPS or another Pi with a public IP), and then you connect to that public server, which tunnels you back to your home Pi. This way, the connection is initiated from the inside out, bypassing router restrictions, you know?
Pros:
- No Port Forwarding: This method truly avoids opening ports on your home router.
- Secure: The SSH connection itself is encrypted.
- Flexible: You can tunnel various services, not just SSH, through this connection.
Cons:
- Requires an Intermediate Server: You need a publicly accessible server that your Pi can connect to. This could be a very small, free-tier cloud instance or another Pi at a different location.
- Complexity: Setting up reverse SSH can be a bit tricky for newcomers.
- Connection Stability: The tunnel might drop, requiring a script to keep it alive.
This method is powerful because your Pi initiates the connection, so your router sees it as outgoing traffic, which is usually allowed. Then, you connect to that public server, and it sends your commands back through the established tunnel to your Pi. It's a bit like having a secret handshake between your Pi and a friend's house, and then you just knock on the friend's door, which is pretty neat.
Free-Tier Cloud-Based Options
Some services offer free tiers that can help you get remote access to your Pi. Tools like ngrok or remote.it create secure tunnels from your local network to their cloud servers, which then expose your Pi to the internet via a unique URL or address. These services handle the tricky parts of network configuration for you, making setup relatively straightforward, so it's a very simple approach.
Pros:
- Easy Setup: Often just a few commands to get going.
- No Router Configuration: They handle the public exposure, so you don't touch your router settings.
- Quick Access: Get a public URL or hostname for your Pi very fast.
Cons:
- Limited Free Tiers: Free plans usually have limitations on bandwidth, connection time, or the number of tunnels.
- Reliance on Third-Party: You're depending on an external service, and if they go down, your access goes down.
- Security Concerns: While the tunnels are secure, you are exposing a port to the public internet, even if it's through their service.
These services are great for testing or temporary access. For example, if you just want to show off a project to a friend for a few hours, they are perfect. However, for continuous, heavy use, the free tiers might not be enough, and you might hit limits, which is something to consider. Still, for occasional use, they are the best choice for simplicity.
MQTT Brokers and Home Automation Platforms
For IoT specifically, using a Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) broker is a very common and effective pattern. MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol perfect for small devices like the Raspberry Pi. Your Pi can publish data to an MQTT broker (which can be hosted publicly for free, or even on another Pi with a public IP) and subscribe to commands from it. Your remote device also connects to the same broker to send commands or receive data.
Pros:
- Designed for IoT: MQTT is highly efficient for low-bandwidth, intermittent connections.
- Scalable: Can handle many devices communicating.
- Event-Driven: Great for real-time control and data updates.
- Free Options: Many public MQTT brokers offer free tiers, or you can host your own.
Cons:
- Not Direct Access: You're not directly "logging into" your Pi; you're sending messages to it.
- Requires Application Logic: Your Pi's programs need to be set up to send and receive MQTT messages.
- Security of Broker: If using a public broker, ensure your topics are secure and authenticated.
Combine this with a home automation platform like Home Assistant, which can also run on a Raspberry Pi, and you have a very powerful setup. Home Assistant can communicate with your local IoT devices, and then you can use Home Assistant's remote access features (some of which are free, like setting up your own DuckDNS and Let's Encrypt certificates) to control everything. This is a very popular way to manage smart homes, and it works incredibly well for free, basically. Learn more about Raspberry Pi projects on our site, and check out this page for more IoT ideas.
Prioritizing Security: Keeping Your IoT Safe
No matter which method you choose for remote access, security should always be a top concern. Letting devices talk to the outside world means you need to be extra careful to protect your home network. It's like making sure your front door is always locked, even if you're just stepping out for a minute, you know?
Strong Passwords and Key-Based Authentication
The first and simplest step is to use strong, unique passwords for your Raspberry Pi and any services you use. Avoid default usernames like 'pi' and default passwords. Even better, use SSH key-based authentication instead of passwords for SSH access. This means you use a pair of cryptographic keys, one on your remote device and one on your Pi, to prove your identity. It's far more secure than a password, and almost impossible to guess, in a way.
Regular Updates and Patches
Software often has little weaknesses that bad actors try to exploit. Developers constantly release updates to fix these. Make it a habit to regularly update your Raspberry Pi's operating system and any software you're running. This keeps your system patched against known vulnerabilities. It's like getting regular check-ups for your car; it keeps things running smoothly and safely, you know?
Limiting Access and Firewalls
Only allow access to your Raspberry Pi from specific IP addresses if possible, especially if you're using something like SSH. On your Pi, use a firewall (like UFW - Uncomplicated Firewall) to block all incoming connections except for those you specifically need. For example, if you're only using SSH, only allow SSH traffic. This minimizes the "attack surface" – the number of ways someone could try to get in. It's a very simple step that makes a big difference.
Getting Started: A Gentle Path
Diving into remote IoT might seem a bit much at first, but with a Raspberry Pi, it's actually a very rewarding experience. You're building something real and useful. Here's a little guide to help you get going, so you know what to expect.
What You'll Need
- A Raspberry Pi: Any model will likely do, but a newer one like a Pi 3 or 4 will give you better performance.
- A MicroSD Card: At least 8GB, for the operating system.
- Power Supply: The correct one for your Pi model.
- Internet Connection: For your Pi and your remote device.
- Basic Computer Skills: Familiarity with command lines helps, but many guides are beginner-friendly.
Basic Setup Steps
First, you'll need to install an operating system on your Raspberry Pi, usually Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian). You can use the Raspberry Pi Imager tool, which makes this very simple. Once the OS is on the SD card, put it in your Pi, connect it to power and your network, and boot it up. You'll want to enable SSH on your Pi, which is usually done through the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool or a simple command, actually.
After that, connect your Pi to your home network, either with an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. Make sure it can access the internet. You can test this by trying to browse a website or ping a public server. Knowing your Pi's local IP address is also helpful, as you'll use it to connect to your Pi from within your home network to start, you know?
Choosing Your Method
Think about what you need most. If you want full, secure access to your entire home network, then a self-hosted VPN is the best choice. If you just need to send commands to a specific IoT device and receive data, MQTT is probably the way to go. For quick, temporary access, a free-tier cloud service might be just what you need, so it's worth thinking about.
Each method has its own set of instructions, but there are tons of free guides and tutorials available online. Pick one that sounds interesting and start small. You don't have to master everything at once. Just getting one remote connection working will feel like a huge win, which it totally is!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions people ask about remote IoT with Raspberry Pi, especially when it's behind a router and you want to do it for free.
How can I access my Raspberry Pi from outside my home network without port forwarding?
You can use methods like reverse SSH tunneling, where your Pi initiates an outgoing connection to a public server, and you connect to that server to reach your Pi. Services like ngrok or remote.it also create tunnels from your Pi to their cloud, letting you access it via a public URL without touching your router's port settings, which is pretty convenient.
What are the safest free methods for remote Raspberry Pi IoT control?
Self-hosted VPNs like OpenVPN or WireGuard offer very high security because all traffic is encrypted and you control the server. SSH key-based authentication is also much safer than passwords. Always keep your Pi's software updated and use a firewall to limit access, as a matter of fact.
Are there any free open-source platforms for managing Raspberry Pi IoT devices remotely?
Yes, absolutely! Home Assistant is a very popular open-source home automation platform that can run on a Raspberry Pi. When combined with a self-hosted MQTT broker like Mosquitto, it provides a powerful and free way to manage and control your IoT devices from anywhere, and it's quite flexible.
Best RemoteIoT Behind Router Raspberry Pi Free Setup For Hobbyists And Enthusiasts

Best RemoteIoT Behind Router Raspberry Pi Free Setup For Hobbyists And Enthusiasts

Best Remote IoT Setup Behind A Router With Raspberry Pi For Free