Running Your RemoteIoT Batch Job Example On AWS: A Practical Guide
Processing data from far-off devices, often called remote IoT, presents some interesting challenges. It's not always about getting every single piece of data right away; sometimes, you just need to gather a lot of information and then process it all at once. This is where a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote setup really shines. It helps you handle large amounts of data efficiently, making sure you get the insights you need without overwhelming your systems.
Think about devices out in the field, perhaps sensors on a farm or equipment in a distant factory. They collect bits of information throughout the day, maybe even for weeks. Sending each tiny bit of data as it happens can be costly and sometimes not even necessary. A batch job, in this situation, waits until there's a good chunk of data, then sends it all at once for processing. This approach, you know, makes a lot of sense for many situations.
This article will walk you through how to set up and manage these kinds of operations on Amazon Web Services (AWS). We'll look at the tools that help you collect, store, and process your remote IoT data effectively. So, if you're wondering how to make your distant devices work smarter, this guide offers some good ideas for a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote approach.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Remote IoT Data
- Why Batch Processing is a Good Idea
- AWS Services for Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- A Simple Remote IoT Batch Job Example on AWS
- Making It Work: Best Practices
- Handling Common Challenges
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Next Steps for Your Remote IoT Data
Understanding Remote IoT Data
Remote IoT data comes from devices that are, well, remote. This means they might not always have a stable internet connection. They could be in places with limited power, or where it is very expensive to send data all the time. Think about weather stations in faraway mountains, or sensors tracking wildlife in a forest. These devices collect data, but they often hold onto it for a while. Then, they send it in bigger chunks when a connection is available, or at scheduled times. This is a bit different from, say, a smart home device that sends data constantly. The nature of this data collection makes batch processing a very good fit, you know, for these kinds of setups.
The data itself can vary a lot. It might be temperature readings, humidity levels, GPS coordinates, or even simple counts. What matters is that it accumulates over time. When you get this data, it's often in a raw form. It needs cleaning, organizing, and sometimes combining with other data before it becomes truly useful. So, understanding the source and the type of data is the first step in planning your remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system. It's almost like preparing ingredients before you cook; you need to know what you have.
Why Batch Processing is a Good Idea
Batch processing is simply gathering data over a period and then processing it all together. For remote IoT, this approach has several big advantages. One main benefit is cost savings. Sending small bits of data frequently can add up in terms of network usage and cloud service charges. Sending data in larger, less frequent batches can significantly cut these costs. It's like sending one big package instead of many small letters; it is usually cheaper.
Another benefit is efficiency. When you process data in batches, you can often use cloud resources more effectively. Instead of having services running all the time waiting for small data points, you can spin up powerful resources only when a batch is ready. This means you only pay for what you use, when you use it. This method also helps with network reliability. If a device is in a spot with a shaky connection, it can store data locally and send it when the connection is strong enough. This reduces the chance of data loss. This is, you know, a pretty smart way to handle things.
Batch processing also simplifies data management for very large datasets. It allows for scheduled analysis, which is great for reports or long-term trend analysis. You can set up jobs to run daily, weekly, or monthly, processing all the accumulated data. This makes it easier to keep track of information over time and find patterns that might not be obvious from real-time data. For a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote setup, this kind of scheduled processing is often the most practical way to go.
AWS Services for Remote IoT Batch Jobs
AWS offers a wide range of services that fit together nicely to build a robust remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system. Each service plays a specific part, from collecting data to processing it and getting useful results. We'll look at some of the main ones you'd typically use.
AWS IoT Core: The Data Collector
AWS IoT Core acts as the central hub for your IoT devices. It lets your remote devices connect securely and send their data. Devices can publish messages to specific topics, which IoT Core then routes. For batch jobs, devices might send compressed files or larger messages less often. IoT Core can also help manage your devices, making sure they are authenticated and authorized to send data. This is the first point of contact for your data, so it is quite important.
Amazon S3: Your Data Storage Spot
Amazon S3, or Simple Storage Service, is where you store all your raw IoT data. It is highly durable and scalable, meaning it can hold vast amounts of data without you having to worry about running out of space. When your devices send their batch data through IoT Core, a common practice is to send it directly to an S3 bucket. S3 is perfect for this because it can handle many uploads at once and store files of any size. It's like a huge digital warehouse for all your information, really.
AWS Lambda: For Quick Processing
AWS Lambda lets you run code without needing to manage servers. This is perfect for event-driven processing. When a new batch file arrives in S3, Lambda can automatically start a function to process it. For a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote, Lambda can trigger small tasks, like decompressing files, validating data, or kicking off a larger processing workflow. It's very cost-effective because you only pay when your code runs. This makes it a great choice for tasks that don't need to run all the time, just when new data shows up.
AWS Glue: For Data Preparation
AWS Glue is a serverless data integration service. It helps you prepare your data for analytics. Glue can discover the schema of your data (what columns it has, what type of data is in them), transform it, and move it to other data stores. For batch processing, Glue is often used to clean and standardize the raw data from S3. It can convert data formats, remove errors, and combine different datasets. This prepares the data for deeper analysis, making it much more useful. It's almost like a data cleaning and organizing service, which is very helpful.
AWS Step Functions: For Orchestration
AWS Step Functions helps you coordinate multiple AWS services into serverless workflows. You can define a series of steps, and Step Functions will make sure they run in the right order, handling errors and retries. For a complex remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote, Step Functions can manage the entire flow: from detecting a new file in S3, to triggering Lambda functions, running Glue jobs, and even sending notifications. It provides a visual way to see your workflow, which makes it easier to build and troubleshoot. This is, you know, a very powerful tool for making sure everything happens as it should.
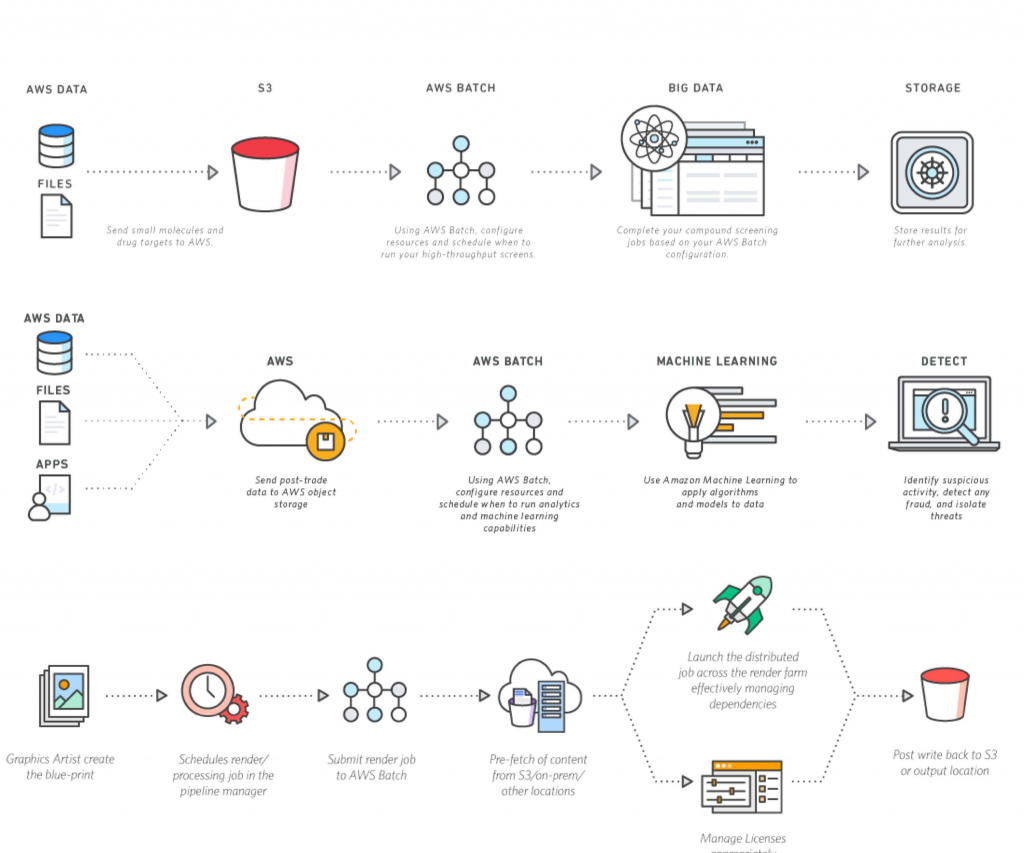
A Simple Remote IoT Batch Job Example on AWS
Let's walk through a conceptual example of a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote setup. Imagine you have a fleet of environmental sensors in remote locations. These sensors collect temperature, humidity, and air quality data every hour. To save battery and data costs, they store this data locally for 24 hours. Once a day, at a specific time, each sensor compresses its collected data into a single file and sends it to AWS. This setup is quite common, and it helps manage resources effectively.
Step 1: Getting Data From Your Devices
Your remote environmental sensors use AWS IoT Core to send their daily data files. Each sensor is set up with proper security certificates, making sure only authorized devices can connect. When it's time to send data, the sensor connects to an IoT Core endpoint and publishes its compressed data file to a specific MQTT topic, say, `iot/sensors/batch_data`. This is, you know, the first step in getting the data from the field to the cloud.
Step 2: Storing It Safely
An AWS IoT Core Rule is set up to listen for messages on the `iot/sensors/batch_data` topic. When a message arrives, this rule takes the incoming data and saves it directly into an Amazon S3 bucket. The rule can even add metadata, like the device ID and the timestamp of when the data arrived. This S3 bucket acts as your raw data landing zone. All the daily batch files from all your sensors will accumulate here. This is, apparently, a very common way to handle incoming IoT data.
Step 3: Starting the Batch Process
Once a new batch file lands in the S3 bucket, an event notification is triggered. This notification can be configured to start an AWS Lambda function. This Lambda function is quite small; its main job is to kick off the next, larger step of the processing workflow. Instead of doing all the heavy lifting itself, it acts as a starter. This separation of duties helps keep things clean and manageable. This is, in a way, like ringing a bell to start a race.
Step 4: Doing the Work
The Lambda function from Step 3 then starts an AWS Step Functions workflow. This workflow is designed to handle the entire batch processing sequence. The first step in the workflow might be another Lambda function that decompresses the incoming data file from S3. After decompression, the workflow could trigger an AWS Glue job. This Glue job reads the raw data, cleans it, transforms it into a standardized format (like Parquet), and then saves the processed data into another S3 bucket, perhaps one designated for "clean data." The Glue job might also update a Glue Data Catalog, which helps you easily query the data later. This is where the real data magic happens, you know, transforming raw bits into something useful.
Step 5: Getting Results
Once the Glue job finishes, the Step Functions workflow can trigger a final Lambda function. This function might send a notification that the batch job is complete, perhaps to an administrator via email or Slack. The processed data in the "clean data" S3 bucket is now ready for analysis. You could use Amazon Athena to run SQL queries directly on this data, or load it into a data warehouse like Amazon Redshift for more complex analytics and reporting. This entire flow illustrates a complete remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system, from device to actionable insights. This is, basically, the end goal of all that data movement.
Making It Work: Best Practices
Building a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system involves more than just picking services. There are some good practices that can make your system more reliable, cost-effective, and easier to manage. Following these tips can save you headaches down the road. It's like building a house; you want a strong foundation, you know?
Data Formatting is Important
Decide on a consistent data format for your devices to send. JSON or CSV are common choices. Make sure the data is structured in a way that is easy to parse and process later. Using a consistent schema across all your devices simplifies the processing steps in AWS Glue or Lambda. Also, consider compressing your data before sending it from the device. This saves on transmission costs and time. GZIP or Snappy are popular compression methods. A well-thought-out data format makes everything else flow much more smoothly.
Security First, Always
Security is paramount for any IoT solution. Ensure your devices use strong authentication methods, like X.509 certificates, with AWS IoT Core. Implement strict access controls (IAM policies) for all your AWS services. Only give services and users the minimum permissions they need to do their job. Encrypt your data both when it's moving (in transit) and when it's stored (at rest) in S3. This protects your valuable information from unauthorized access. This is, honestly, one of the most important things to get right.
Cost Awareness Helps
AWS services are powerful, but costs can add up if not managed well. For a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote, focus on serverless services like Lambda, S3, and Glue, as you only pay for what you use. Optimize your batch sizes and frequency to reduce the number of times you trigger services. For example, sending one large batch daily is usually cheaper than many small batches throughout the day. Monitor your AWS billing dashboard regularly to keep an eye on expenses. This helps you stay within budget, which is pretty important for any project.
Error Handling is Key
Things can go wrong. Devices might send malformed data, network connections might drop, or a processing step might fail. Design your workflow with robust error handling. AWS Step Functions has built-in retry mechanisms and error states that you can use. Set up dead-letter queues (DLQs) for Lambda functions to catch messages that fail processing. Implement logging for all your services so you can easily track down issues. Knowing what went wrong and why is crucial for maintaining a reliable system. It's like having a backup plan for everything, you know.
Monitoring Your Jobs
Once your batch job system is running, you need to monitor its health and performance. Use Amazon CloudWatch to collect logs and metrics from your AWS services. Set up alarms to notify you of failures, long processing times, or unexpected activity. Monitoring helps you spot problems early and ensure your data is being processed correctly and on time. Regularly reviewing your logs can also give you insights into how to optimize your system further. This is, basically, how you keep everything running smoothly.
Handling Common Challenges
Even with a well-designed remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system, you might run into a few common hurdles. One challenge is dealing with data volume spikes. Sometimes, many devices might send data at the same time, or a single device might send a much larger file than usual. AWS services are generally scalable, but it's good to design your system to handle these bursts gracefully, perhaps by allowing for temporary queues or increasing concurrent processing limits. This helps prevent bottlenecks.
Another challenge is data quality. Remote devices can sometimes send corrupted or incomplete data. Your processing workflow, especially the AWS Glue part, needs to be robust enough to identify and either fix or discard bad data. Implementing data validation checks early in the process can save a lot of trouble later. Also, managing device software updates can be tricky for remote devices. Ensuring your devices can reliably send data after an update is a continuous process. This is, you know, a bit like keeping all the pieces of a puzzle in good shape.
Finally, keeping track of device state for millions of devices can be a bit overwhelming. While batch processing handles the data, knowing which devices are online or offline, or if they have sent their data, requires a separate management strategy. AWS IoT Device Management can help here. It's about more than just data; it's about the devices themselves. This is, arguably, a continuous effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
People often ask about remote IoT batch jobs. Here are some common questions and their answers:
How much does it cost to run a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote setup?
The cost really depends on how much data you process and which services you use. Services like AWS Lambda and S3 are pay-as-you-go, so you only pay for the resources you consume. Processing large amounts of data with AWS Glue or running many Step Functions workflows will increase costs. You can use the AWS pricing calculator to estimate your expenses based on your expected data volume and processing needs. It's a very flexible system, so costs can vary quite a bit.
Can I process data in real-time instead of batches?
Yes, you certainly can! AWS offers services like Kinesis and IoT Analytics that are designed for real-time or near real-time data processing. However, for remote IoT devices with limited connectivity or power, or where immediate insights aren't necessary, batch processing is often more practical and cost-effective. It really depends on your specific use case and what your devices can support. For some situations, real-time is great, but for others, batch is just better, you know?
What if my remote devices lose connection and can't send data?
This is a common concern. For a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote, devices are often designed to store data locally if they lose connection. Once the connection is restored, they can then send all the accumulated data in a single batch. This local storage capability is very important for ensuring data reliability in unstable network environments. You should design your device firmware to handle these offline periods gracefully. This is, in a way, like having a temporary storage unit on the device itself.
Next Steps for Your Remote IoT Data
Setting up a remoteiot batch job example remote aws remote system can seem like a big project, but by breaking it down into smaller pieces, it becomes quite manageable. Start by clearly defining what data your devices collect and how often it needs to be processed. Then, think about the specific AWS services that fit each part of your workflow. This approach lets you build a powerful and efficient system for handling data from your far-off devices. It is, basically, about taking one step at a time.
Consider starting with a small pilot project. Get one or two devices sending batch data to S3, then build out the processing workflow from there. This hands-on approach will help you understand the nuances and optimize your setup. Remember that the goal is to get useful information from your data, so focus on the insights you want to gain. You can learn more about AWS IoT Core on our site, and link to this page for more details on data storage options. There's a lot to explore, and the possibilities are quite exciting for managing your remote data effectively.
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remote IoT Batch Job Example: Revolutionizing Automation With AWS