Getting Up To Speed: Your Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Since Yesterday
Have you ever thought about how much data your smart devices or industrial sensors collect every single day? It's a lot, isn't it? From temperature readings in a remote warehouse to the operational status of machinery far away, keeping track of all this information can feel like a big job. This is where a remote IoT batch job comes into play, especially when you need to process data that's been sitting there, say, since yesterday. It's a pretty neat way to handle large amounts of information from devices that aren't right next to you.
Picture this: you have hundreds, maybe thousands, of tiny sensors scattered across different places. Each one is quietly gathering bits of data. Now, you don't always need to know what's happening the very second it happens. Sometimes, you just need to gather everything that occurred over a specific period, like the last 24 hours. That's exactly what we're talking about with a "remote IoT batch job example remote since yesterday." It's about collecting, processing, and making sense of that historical data in one go, rather than trying to deal with each tiny piece as it arrives. This approach, you know, makes things much more manageable.
We'll look at why these kinds of jobs are so useful, what goes into setting one up, and some of the things you might want to think about to make sure it runs smoothly. It's a way to get valuable insights from your far-off devices without constant, real-time connection, which can be pretty efficient. So, let's explore how these systems work and why they're becoming more and more common in today's connected world.
Table of Contents
- What is a Remote IoT Batch Job?
- Why Are These Jobs So Important?
- Challenges of Running Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- A Practical Look: Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Since Yesterday
- Tips for Successful Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Common Questions About Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Remote IoT Processing
- Final Thoughts and Next Steps
What is a Remote IoT Batch Job?
To really get a handle on a remote IoT batch job, we should probably break down each part of the phrase. It helps to see how all the pieces fit together. This way, you know, we can appreciate the whole picture.
Defining Batch Jobs
A batch job is, in a way, like doing your laundry. You gather up all your dirty clothes, put them in the machine, and run it all at once. You don't wash each sock individually as it gets dirty, right? Similarly, a batch job collects a bunch of tasks or data, then processes them together in one go. This often happens at a scheduled time, perhaps overnight or during off-peak hours, when system resources are more available. It's a very common way to handle lots of data or repetitive tasks.
These jobs are really good for things that don't need instant attention. For example, generating daily reports, updating large databases, or performing complex calculations that would take too long if done one piece at a time. They can be set up to run automatically, which is pretty convenient, too.
What Makes it "Remote IoT"?
Now, add "remote IoT" into the mix. "IoT" stands for the Internet of Things, which refers to all those physical objects that have sensors, software, and other technologies built into them. These things connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. Think about smart thermostats, connected factory machines, or even agricultural sensors out in a field. They are all, you know, part of the IoT.
"Remote" simply means these IoT devices are not physically in the same place as the central system that manages them. They could be across town, in another state, or even on a different continent. So, a "remote IoT" setup means you're dealing with devices that are far away, sending their data back to a central point. This distance, you might say, adds a few interesting considerations.
Why "Since Yesterday"?
The "since yesterday" part is important because it defines the time frame for the data you want to process. Instead of getting a live feed, you're interested in all the data that accumulated from a specific past point up until now. This is really useful for looking at trends, checking daily summaries, or making sure all the previous day's information is accounted for. It's a way to catch up, so to speak, on what happened when you weren't actively watching. This kind of historical view is, in some respects, very valuable.
For instance, if you have environmental sensors in a remote forest, you might not need to know the temperature every minute. But you would probably want a daily summary of temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and maybe even air quality from the past 24 hours. A batch job "since yesterday" would gather all that information for you efficiently. It gives you a snapshot of what occurred, which is pretty helpful for long-term analysis.
Why Are These Jobs So Important?
Remote IoT batch jobs play a pretty big role in how businesses and organizations use their connected devices. They offer several advantages that make them a preferred method for many data processing needs. You know, there are some really good reasons to use them.
Data Consistency and Accuracy
When you gather data in batches, you can make sure all the information from a specific period is processed together. This helps maintain data consistency, meaning all your records line up correctly. It also gives you a chance to check for errors or missing pieces before the data is used for reports or decisions. This is, actually, quite important for reliable insights.
Imagine trying to reconcile inventory data from multiple remote auto parts stores, each dealing with items like a 2017 Subaru Legacy front seat or a used 2005 Subaru Legacy GT sedan seat set. If you process each sale as it happens, it can be hard to get a complete picture. But if you collect all sales and stock changes from "since yesterday" in one batch, you can run checks to ensure everything balances out, giving you a much more accurate inventory count across all locations. It just helps keep things honest, you know.
Efficiency and Resource Use
Running a batch job is often more efficient than processing data in real-time, especially for large volumes. Instead of constantly opening and closing connections to remote devices or systems, you open them once, pull all the necessary data, and then process it. This saves on network bandwidth, computing resources, and even power consumption on the devices themselves. It's like sending one big truck instead of many small cars to pick up packages. This can be, pretty much, a big saver.
For devices with limited battery life or intermittent connectivity, this method is especially good. They can store data locally throughout the day and then send it all during a scheduled batch window when conditions are favorable. This means less strain on the device and a more reliable data transfer. So, it's a smart way to manage your resources, you know.
Historical Analysis and Insights
Processing data "since yesterday" gives you a clear historical record. This is incredibly valuable for spotting trends, understanding performance over time, and making predictions. You can look back at daily patterns in temperature, machine usage, or even traffic flow to identify anomalies or areas for improvement. This kind of insight is, arguably, what makes data truly useful.
For example, if you're monitoring a fleet of vehicles, a batch job could collect all engine diagnostics and mileage data from each vehicle since the last day. This allows you to analyze fuel efficiency trends, predict maintenance needs, or even track driver behavior over time. It helps you see the bigger picture, in a way.
Operational Continuity
Batch jobs can run in the background without interrupting day-to-day operations. This means your devices can continue doing their primary jobs while the data collection and processing happen quietly. It also means that if there's a temporary network outage or a system hiccup, the data can simply wait until the next batch run. This helps ensure that your operations keep moving along, which is, basically, what everyone wants.
You don't want your critical systems to slow down or stop just because they're trying to send every piece of data the moment it's generated. Batch processing helps keep the main show running smoothly. It's a bit like having a dedicated team working overnight to prepare everything for the next day, so the daytime crew can focus on their tasks without interruption. This is, you know, a pretty good setup.
Challenges of Running Remote IoT Batch Jobs
While remote IoT batch jobs offer many benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. It's important to be aware of these so you can plan for them. You know, it's not always a straight shot.
Connectivity Issues
Remote devices, especially those in distant or harsh environments, might not always have a stable internet connection. This can make it tricky to ensure all data is sent and received successfully during a batch window. You might have to deal with dropped connections or very slow transfer speeds. This is, quite frankly, a common headache.
Designing your system to handle intermittent connections is key. This could involve having devices store data locally until a connection is available, or implementing retry mechanisms for data transfers. It's about being prepared for when the network decides to take a little break, in a way.
Security Concerns
Whenever data travels over a network, especially from remote locations, security is a big deal. You need to make sure the data is encrypted both when it's being sent and when it's stored. Unauthorized access to your IoT devices or the data they send could lead to serious problems. This is, definitely, something you want to get right.
Implementing strong authentication for devices, using secure communication protocols, and regularly updating security measures are all vital steps. You're basically building a very strong fence around your data, you know, to keep it safe.
Data Volume and Processing
Even though batch processing is efficient, the sheer volume of data collected "since yesterday" from many devices can still be enormous. This requires robust infrastructure to store and process it all. You need powerful servers and databases that can handle the load without slowing down. This can be, literally, a lot of data.
Planning for scalability is crucial. What works for 100 devices might not work for 10,000. You need systems that can grow with your data needs. It's like planning for a crowd; you need enough space for everyone, even if more people show up than you expected, so.
Device Heterogeneity
It's common to have different types of IoT devices, perhaps from various manufacturers, all sending data. These devices might use different communication protocols or data formats. Getting them all to play nicely together in a single batch job can be a real puzzle. It's a bit like trying to get everyone to speak the same language, you know.
You might need to use data standardization techniques or translation layers to convert all incoming data into a consistent format before processing. This adds a layer of complexity but is often necessary for effective analysis. It helps make sure everyone is on the same page, in a way.
Error Handling and Retries
Things can and will go wrong. A device might fail to send its data, a network connection might drop midway through a transfer, or a processing step might encounter an issue. A well-designed batch job needs to anticipate these problems and have mechanisms to handle them gracefully. This is, essentially, about being prepared for the unexpected.
This includes automatic retries for failed transfers, logging detailed error messages, and alerting administrators when something goes seriously wrong. You want to make sure that even if a part of the job fails, the whole thing doesn't fall apart, you know. It's about building resilience into your system.
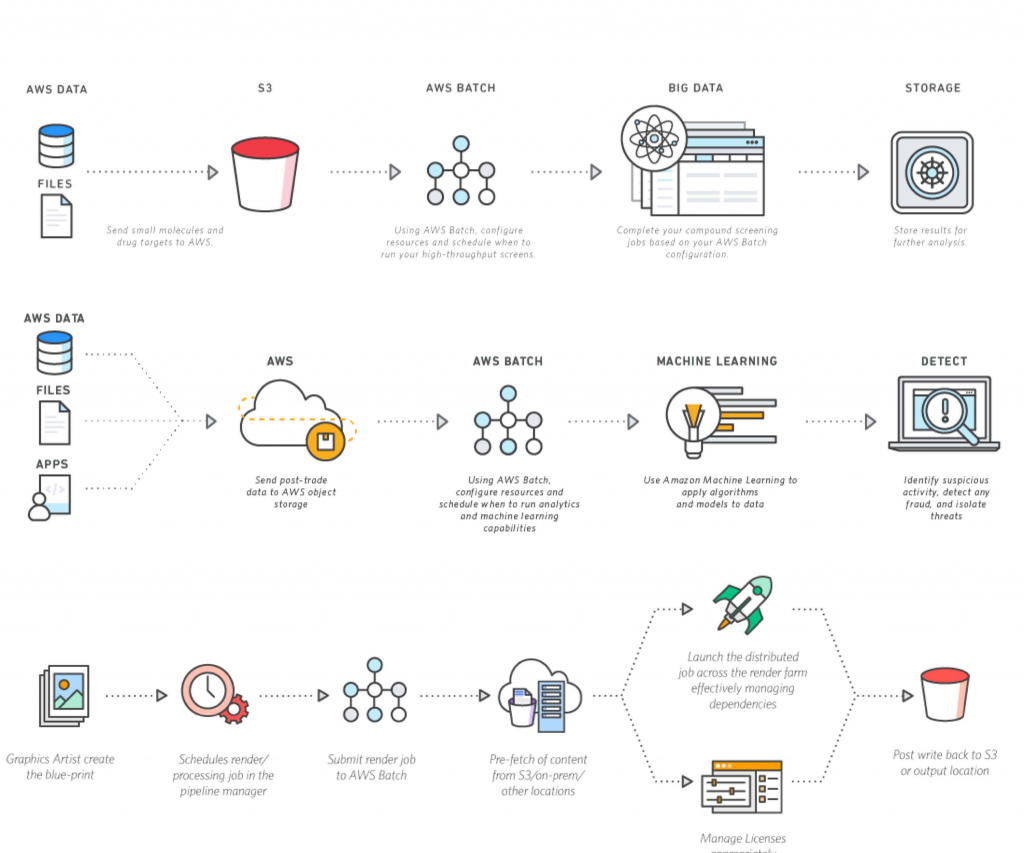
A Practical Look: Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Since Yesterday
Let's walk through a concrete example to see how a remote IoT batch job processing data "since yesterday" might actually work. This will give you a better feel for it. It's pretty interesting, if you ask me.
Scenario Setup
Imagine a large utility company that manages thousands of smart electricity meters spread across a wide geographical area. These meters are IoT devices, located in homes and businesses, often in remote or hard-to-reach places. They continuously record electricity consumption. The company needs to collect this consumption data daily for billing, grid management, and anomaly detection. They don't need real-time data for every single meter, but they do need accurate daily totals. This is, more or less, a very common scenario.
Similarly, think about a network of used auto parts dealers. They have inventory systems at each location, perhaps tracking items like a 2017 Subaru Legacy front seat or a 2005 Subaru Legacy GT sedan seat set. A batch job could gather all sales and stock adjustments from each remote dealer since yesterday, consolidating this information into a central database. This ensures the main inventory system knows exactly what's available across the entire network, even if individual locations have intermittent internet access. It just helps keep everything organized, you know.
The "Since Yesterday" Process
Every night, usually between midnight and 3 AM when network traffic is low, the utility company's central system initiates a remote IoT batch job. The goal is to collect all electricity consumption readings from each smart meter from 12:00 AM yesterday until 11:59 PM yesterday. This ensures a full 24-hour cycle of data is captured. It's a pretty straightforward way to

Remote IoT Batch Jobs: Explained & AWS Examples

Remote IoT Batch Jobs: Explained & AWS Examples
Remote IoT Batch Jobs: Explained & AWS Examples