Remote IoT Batch Job Example In AWS Remote: Streamlining Connected Operations
Imagine keeping countless devices in sync, no matter how far apart they are. Think about the sheer scale of managing something like fuel distribution for Sunoco across more than 40 U.S. states, Puerto Rico, Europe, and Mexico, with all those gas stations needing updates or data collection. Or, consider the challenge of supporting millions of active users and creators on platforms like Roblox, where devices from smartphones to VR headsets are all connected. Processing information or sending out instructions to such widespread systems calls for smart, automated ways to get things done. This is precisely where a remoteiot batch job example in aws remote really helps.
These kinds of jobs are a big deal for anyone dealing with many connected gadgets. They let you send commands or gather data from a large group of devices all at once, even if those devices are scattered all over the globe. It's about making sure your connected equipment works as it should, without you having to touch each one individually, which is pretty much impossible with a huge number of them, you know?
So, we're going to look at how a remote IoT batch job works in AWS. We'll explore why this approach is so useful, what services you might use, and even walk through a simple idea of how you could set one up. It's a way to keep your operations smooth and your devices humming along, which is something every business with distributed assets needs to think about, very much so.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Why AWS for Remote IoT Batch Jobs?
- A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example in AWS Remote
- Best Practices for Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Remote Device Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Remote IoT Batch Jobs
What They Are and Why They Matter
A remote IoT batch job is, in a way, like sending out a mass email to all your connected devices. Instead of an email, you're sending a set of instructions or a software update. It's about performing an action on many devices at once, without needing to interact with each one individually. This is incredibly useful because it saves a ton of time and effort, especially when you have hundreds or thousands of devices out there, you know?
These jobs matter because they help keep your device fleet healthy and secure. Think about security patches or new features; you want all your devices to get them quickly. Doing this manually would be a nightmare. Batch jobs automate this process, making sure your whole system stays up-to-date and works correctly, which is pretty important.
Common Scenarios Where They Are Helpful
There are many times when a remote IoT batch job really shines. For example, if you need to update the software on all your smart thermostats, a batch job can push out that new version to every single one. Or, perhaps you need to change a setting on a group of industrial sensors; a batch job handles that with ease, too it's almost.
Another common use is gathering specific data from devices, like collecting log files for troubleshooting. Instead of connecting to each device separately, you can tell them all to upload their logs to a central spot. This also helps with device resets or reboots, making sure they start fresh when needed. It's a very flexible tool for managing a widespread network.
Why AWS for Remote IoT Batch Jobs?
Benefits of Using AWS IoT Services
AWS offers a strong set of tools for managing connected devices, which makes it a good choice for remote IoT batch jobs. One big benefit is scalability; you can start small and grow to millions of devices without much trouble. AWS handles the heavy lifting of keeping connections stable and secure, which is rather nice.
Another plus is the way AWS services work together. You can easily combine different parts of AWS to build a complete solution, from connecting devices to processing their data and sending commands. This integration means less work for you in setting things up, and more time focusing on what your devices actually do, you see.
Key AWS Services Involved
When you're working with a remote IoT batch job example in AWS remote, you'll likely use several key services. AWS IoT Core is the main hub for connecting devices and sending messages. It's where your devices talk to the cloud, so.
Then there's AWS IoT Jobs, which is specifically for managing and tracking these batch operations. It lets you define what action to take and which devices should receive it. You might also use AWS Lambda for custom logic, Amazon S3 for storing data or firmware updates, and Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring how your jobs are doing, that is that.
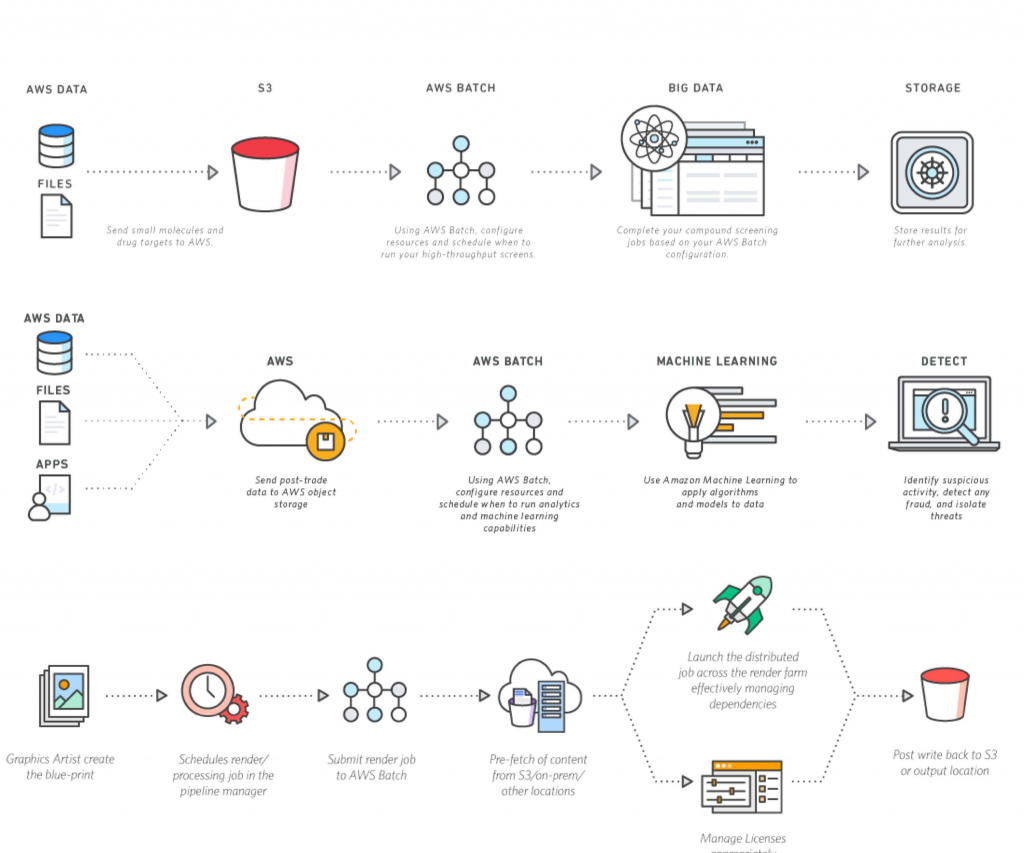
A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example in AWS Remote
Setting Up the Environment (Briefly)
Before you can run a batch job, your devices need to be set up to talk to AWS IoT Core. This means giving them unique identities and security credentials, like certificates. Each device needs to know how to connect and authenticate itself, which is a bit like giving it a passport to enter the AWS cloud, you know?
You'll also need to make sure your devices have the right software on them to receive and act on commands from AWS IoT Jobs. This usually involves a small piece of code that listens for incoming messages and then performs the requested action, whatever that might be, you see.
Defining the Job: An Update Task
Let's consider a simple remoteiot batch job example in aws remote: updating the firmware on a group of remote sensors. First, you'd prepare the new firmware file and upload it to an Amazon S3 bucket. This bucket acts as a secure storage place for your update, so.
Next, you'd create a "Job Document" in AWS IoT Jobs. This document is basically a set of instructions for your devices. It would tell them where to find the new firmware in S3, how to download it, and what steps to take to install it. You can specify details like timeout periods and how many retries a device should attempt if something goes wrong, too it's almost.
Targeting Devices for the Job
Once your job document is ready, you need to tell AWS IoT Jobs which devices should receive it. You can target devices in a few ways. You might use a "thing group," which is a collection of devices you've organized together, perhaps by location or type. For instance, all your Sunoco gas station fuel pump sensors in a specific region could be in one group, or all Roblox VR headsets, that is that.
Alternatively, you can provide a list of individual device names. AWS IoT Jobs then sends a notification to each targeted device, letting it know there's a new job waiting. The device then connects back to AWS IoT to fetch the job details and start the update process, which is pretty clever.
Monitoring Job Progress
As the job runs, you'll want to keep an eye on its progress. AWS IoT Jobs provides dashboards and metrics that show you how many devices have started the job, how many have finished successfully, and how many have failed. This real-time visibility is very important for knowing if your update is going smoothly, you know?
You can also set up alerts using Amazon CloudWatch. For example, if too many devices fail the update, you could get a notification. This helps you react quickly to any problems and address them before they affect too many of your operations, which is rather helpful.
Handling Failures and Retries
Devices can sometimes go offline or encounter issues during an update. AWS IoT Jobs has built-in features to help with this. You can configure the job to retry failed updates a certain number of times. For example, if a device is temporarily disconnected, it might try again when it comes back online, so.
For more complex failures, you can set up error handling. This might involve sending a notification to a developer or triggering a Lambda function to perform a specific recovery action. Understanding why jobs fail and having a plan for those failures is a big part of running a good remoteiot batch job example in aws remote, you see.
Best Practices for Remote IoT Batch Jobs
Security Considerations
Security is always a top concern when dealing with connected devices. Make sure your devices use strong authentication methods, like X.509 certificates, to connect to AWS IoT Core. Also, use the principle of least privilege: give your devices only the permissions they absolutely need to do their job, and nothing more, you know?
Encrypt all data both in transit and at rest. When devices download firmware updates from S3, make sure those connections are secure. Regular security audits of your device software and your AWS configurations are also a good idea. Staying on top of security helps keep your entire system safe, very much so.
Scalability Tips
When you're dealing with a large number of devices, like the vast network Sunoco manages or the millions of users Roblox supports, scalability is key. Design your device software to be lightweight and efficient, so it doesn't consume too many resources. Use AWS IoT Core's message brokering capabilities to handle high volumes of traffic, that is that.
Consider breaking down very large batch jobs into smaller ones if necessary. This can help manage the load and make it easier to troubleshoot if something goes wrong. Also, leverage AWS IoT Device Management features like fleet indexing to easily find and group devices for targeting, which is pretty useful.
Error Handling and Retries
Even the best-planned batch jobs can run into problems. Design your device software to report job status and errors back to AWS IoT. This gives you visibility into what's happening on each device. Implement retry logic on the device side for transient network issues, so.
On the AWS side, configure appropriate retry policies for your jobs. Use CloudWatch logs and metrics to identify common failure patterns. You might even set up automated responses to certain errors, perhaps by triggering an AWS Lambda function to attempt a different fix or notify a team, too it's almost.
Versioning Jobs for Better Control
Just like with any software, you'll likely create different versions of your batch jobs over time. Always keep track of which version of a job you're deploying and what changes it includes. This helps with troubleshooting and rollback if a new job causes unexpected issues, you know?
Consider using a consistent naming convention for your job documents and firmware files. This makes it easier to manage and deploy updates, especially as your fleet grows. Good version control gives you more control and predictability over your device operations, very much so.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Remote Device Management
The world of connected devices is always growing, with more and more things getting smart every day. As of late 2023, the need for efficient remote device management is only getting stronger. We'll likely see even more advanced ways to automate tasks, perhaps with AI helping to predict when devices might need maintenance or updates, that is that.
The goal remains the same: to make it easier to keep vast networks of devices working perfectly, no matter their location. Tools like the remoteiot batch job example in aws remote will continue to be essential for businesses that rely on their connected equipment to operate smoothly and effectively. It's a field that's constantly evolving, which is pretty exciting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What kinds of actions can a remote IoT batch job perform?
A remote IoT batch job can perform many actions. It can update device software, change device settings, collect diagnostic logs, or even trigger a device reboot. Basically, any command you can send to a single device, you can send to a whole group using a batch job, you know?
How does AWS IoT ensure devices receive job commands securely?
AWS IoT uses secure communication protocols, like MQTT over TLS, to make sure job commands are sent safely. Devices authenticate using unique certificates or credentials, so only authorized devices can connect and receive instructions. This helps prevent unauthorized access or tampering with your devices, very much so.
Can I schedule a remote IoT batch job to run at a specific time?
Yes, you can schedule a remote IoT batch job. While AWS IoT Jobs itself manages the rollout, you can use other AWS services, like AWS Lambda triggered by Amazon EventBridge (formerly CloudWatch Events), to initiate a job at a predetermined time or based on a specific event. This gives you flexibility in when and how your updates are deployed, so.
Learn more about connected device management on our site, and link to this page for more AWS IoT solutions.

Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remoteiot Batch Job Example Remote Aws Developing A Monitoring