Understanding The **Remote IoT Batch Job Example**: Automating Tasks From Afar
Working from a distance, or remotely, has become pretty common for many types of jobs, you know, like accounting and bookkeeping positions steadily growing. People even join and invite others to remote raids in games. This idea of handling things without being right there, it's actually pretty powerful, and it extends way beyond just office work or gaming. We're talking about getting things done with physical devices, too.
Think about how teams, companies, and individuals share news, experience, and tips about working remotely. There's a whole community for it, whether it's for streaming games via the cloud or nurses interested in working from home. This shift towards doing things from anywhere, it really shapes how we think about tasks and control, especially when you consider physical equipment and sensors.
So, what happens when you combine this "from a distance" approach with the world of connected gadgets? You get something pretty useful: the remote IoT batch job. It's about telling a whole bunch of devices to do something all at once, even if they are scattered all over the place. This can make a lot of sense for businesses that have many sensors or machines out in the field.
Table of Contents
- What is a Remote IoT Batch Job?
- Why These Jobs Matter
- Common Remote IoT Batch Job Examples
- How They Work: The Pieces Involved
- Challenges You Might Face
- Making It Work Well: Good Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Remote IoT Tasks
What is a Remote IoT Batch Job?
A remote IoT batch job is, in essence, a way to get many internet-connected devices to do a specific task at the same time, or in a scheduled group, without someone being physically present with each device. It's like sending out a single instruction that a whole fleet of gadgets will follow. This is pretty useful, you know, for managing a lot of things.
The Remote Part
The "remote" bit means you're not standing next to the equipment. It's a lot like how people are applying for remote data entry or admin assistant jobs through LinkedIn, or how you can stream Xbox games via the cloud even if you don't have an Xbox yourself. You're controlling things from a distance, perhaps from a central office or even your home, which is rather convenient.
This idea of working from afar, it's actually a big part of how many businesses operate now. It means you can manage things across different cities, states, or even countries. So, you might be in one place, and your IoT devices could be spread out far and wide, but you can still give them instructions. It's a really flexible way to handle operations, honestly.
The IoT Part
IoT stands for the Internet of Things. These are everyday objects, or industrial machines, that have sensors, software, and other technologies built into them, allowing them to connect and exchange data over the internet. Think about smart thermostats, factory sensors, or even connected streetlights. They are, you know, everywhere these days.
These devices often collect information or perform specific functions in their environment. They might be checking temperatures, monitoring vibrations, or controlling lights. The key thing is that they can communicate, sending data back and receiving commands. This makes them perfect for getting instructions from a central point, basically.
The Batch Job Part
A "batch job" is simply a program or a set of instructions that runs without human interaction, typically on a group of items. Instead of doing something one device at a time, you group them together and tell them all to do the same thing. This saves a lot of time and effort, naturally.
For example, if you had 1,000 smart light bulbs and wanted to change their brightness setting, you wouldn't go to each one individually. You'd create a batch job to send that instruction to all of them at once. It's a very efficient way to manage many similar tasks, or so it seems.
Why These Jobs Matter
Remote IoT batch jobs are pretty important for several good reasons, especially as businesses grow and have more connected equipment. They bring a lot of good things to the table, in some respects, making operations smoother and more cost-effective. It's about getting more done with less direct effort, you know.
One big benefit is efficiency. Imagine trying to update the software on hundreds or thousands of devices one by one. That would take forever, honestly. With a batch job, you can kick off the process for all of them at once, freeing up people to work on other things. This kind of automation is a big time-saver, actually.
Then there's consistency. When you apply a change to many devices using a single batch job, you make sure that every device gets the exact same instruction. This helps avoid errors that might happen if someone were manually configuring each one. It leads to a more uniform and reliable system, which is quite nice.
Cost savings are another clear advantage. Sending technicians out to every single device location can be very expensive, especially if those locations are far apart. Remote batch jobs cut down on travel and labor costs significantly. It's a pretty smart way to manage expenses, truly.
Finally, scalability is a huge factor. As your network of IoT devices grows, managing them individually becomes nearly impossible. Batch jobs let you handle a few dozen or many thousands of devices with roughly the same amount of effort. This means your operations can grow without becoming overwhelmed, which is pretty cool.
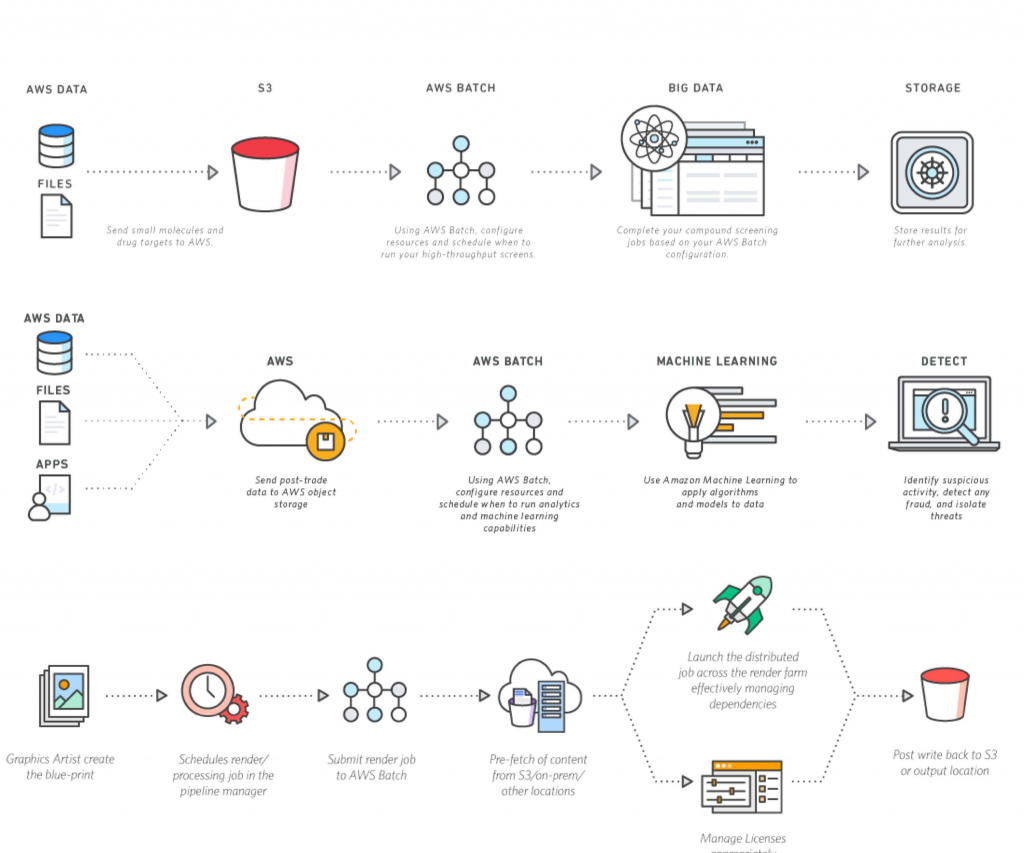
Common Remote IoT Batch Job Examples
To really get a feel for what these jobs do, let's look at some practical scenarios. These examples show how different industries can use this approach to handle their connected equipment from a distance, you know, making things run smoother. They cover a good range of uses, basically.
Updating Device Software
This is probably one of the most common and important uses. Just like your phone or computer needs software updates, so do IoT devices. These updates might bring new features, fix security weaknesses, or improve how the device works. Doing this manually for many devices is a nightmare, so a batch job is perfect.
For instance, a company managing smart streetlights across a city might need to update the firmware on all 10,000 lights. They'd create a batch job to push the new software out to every light, perhaps overnight. This ensures all lights are running the latest, most secure version, and it's done without sending out a crew to each pole, which is pretty efficient.
Another example could be in a factory with hundreds of robotic arms. If a software bug is found, a batch job can quickly send a fix to all affected robots, minimizing downtime. This keeps production flowing and prevents costly interruptions, which is definitely a good thing.
Collecting Data in Bulk
IoT devices are great at gathering data, whether it's temperature readings, machine performance metrics, or environmental conditions. Sometimes, you need to pull specific sets of data from many devices at once for analysis. This is where a remote batch job can help, naturally.
Consider a network of agricultural sensors spread across many farms, monitoring soil moisture and nutrient levels. A research team might schedule a batch job to collect a snapshot of data from all sensors every morning. This gives them a comprehensive overview without having to visit each farm, which saves a lot of time and effort, honestly.
Similarly, a utility company might use batch jobs to pull meter readings from thousands of smart meters at the end of the billing cycle. This automates the data collection process, making billing more accurate and timely. It's a rather straightforward way to get a lot of information, too.
Changing Device Settings
Sometimes, you need to adjust how your IoT devices operate. This could involve changing a threshold, altering a schedule, or activating a new mode. A batch job lets you apply these changes across many devices simultaneously, which is very helpful.
For example, a company managing smart thermostats in a large office building might want to adjust the heating schedule for the upcoming winter season. They could send a batch command to all thermostats to change their programmed settings. This ensures consistent climate control throughout the building with just one action, basically.
In a retail environment, smart display screens might need their content updated or their brightness adjusted based on the time of day or special promotions. A batch job can push these configuration changes to all screens in all stores at once. This keeps the customer experience fresh and consistent, you know.
Security Checks and Audits
Keeping IoT devices secure is super important. Remote batch jobs can be used to run security checks, apply security patches, or even verify device configurations against security policies. This helps keep your network safe from potential threats, which is a big deal, frankly.
A smart city infrastructure, for instance, might have thousands of connected cameras. A security team could schedule a batch job to run a quick security scan on all cameras weekly, looking for any unusual activity or configuration drifts. This proactive approach helps identify and address vulnerabilities quickly, pretty much.
For industrial control systems, a batch job might be used to ensure that all devices have the latest security certificates installed. This helps maintain a strong security posture across the entire operational technology network. It's a critical step for protecting sensitive systems, honestly.
How They Work: The Pieces Involved
Making a remote IoT batch job happen requires a few key parts working together. It's not just one piece of software; it's a whole system that allows you to send commands and receive feedback from devices far away. Understanding these components helps, you know, make sense of it all.
Cloud Platforms
Most remote IoT batch jobs rely heavily on cloud computing services. These platforms provide the infrastructure to connect, manage, and process data from many devices. They offer services specifically designed for IoT, like device registries, message brokers, and data storage. These are, in a way, the central hubs.
Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) all have robust IoT offerings. They allow you to register your devices, monitor their status, and send commands to them, whether individually or in groups. This makes managing a large fleet much more manageable, pretty much.
Device Connectivity
For devices to receive commands and send data, they need a way to connect to the internet and the cloud platform. This could be through Wi-Fi, cellular networks (like 4G or 5G), LoRaWAN, or other specialized IoT communication protocols. The choice depends on the device's location, data needs, and power consumption, you know.
Reliable connectivity is absolutely critical for batch jobs. If a device can't connect, it won't receive the command, and the job will fail for that particular device. So, ensuring a stable connection is a pretty big consideration when setting things up, honestly.
Command and Control Systems
These are the software tools or services that let you create, schedule, and monitor your batch jobs. They provide the interface for you to define what task needs to be done, which devices should do it, and when. This is where you actually tell the system what to do, basically.
Often, these systems are part of the broader cloud IoT platform, but they can also be specialized third-party software. They typically include features for tracking job progress, reporting successes and failures, and handling errors. This helps you keep tabs on everything, which is quite useful.
Scripting and Automation
At the heart of a batch job is the script or code that defines the actual task. This could be a simple command to change a setting or a more complex program to perform a software update. These scripts are then sent to the devices to be executed. They are, in a way, the instructions themselves.
Automation tools help in scheduling these jobs to run at specific times or in response to certain events. This means you can set up jobs to run automatically, perhaps daily or weekly, without manual intervention each time. It takes a lot of the repetitive work out of the equation, you know, which is good.
Challenges You Might Face
While remote IoT batch jobs offer many benefits, they also come with their own set of difficulties. It's not always a completely smooth ride, and being aware of these potential issues can help you plan better, you know. There are a few things that can make these jobs tricky, basically.
One major challenge is inconsistent connectivity. Devices might be in areas with poor network coverage, or their internet connection might drop periodically. If a device isn't connected when a batch job runs, it will miss the instruction. Handling these offline devices requires careful planning, which is pretty important.
Security is another big concern. Sending commands to many devices at once means that if your command system is compromised, an attacker could potentially control your entire fleet. Protecting the communication channels and the command system itself is absolutely critical. You need strong authentication and encryption, honestly.
Device heterogeneity, or having many different types of devices, can also be a hurdle. Not all IoT devices are built the same; they might run different operating systems or have varying capabilities. A batch job designed for one type of device might not work on another, so you need to account for these differences, you know.
Error handling and reporting are also important. What happens if a batch job fails on some devices? How do you know which ones failed and why? Having good mechanisms for logging errors, retrying failed tasks, and notifying administrators is very necessary. It helps you troubleshoot problems effectively, basically.
Making It Work Well: Good Practices
To get the most out of remote IoT batch jobs and avoid common pitfalls, there are several good habits to adopt. These practices help ensure your jobs run smoothly, securely, and effectively, you know. They can make a big difference in how well your system performs, honestly.
Start with thorough planning. Before you run a batch job on many devices, clearly define the goal, the scope, and the expected outcome. Understand the potential impact of the job on device performance and user experience. A little planning goes a long way, basically.
Always test your batch jobs on a small group of devices first, perhaps in a testing environment or on a few non-critical devices. This helps you catch any bugs or unexpected behaviors before rolling out the job to your entire fleet. It's like a pilot program for your commands, you know.
Implement robust monitoring. You need to be able to see the status of your batch jobs in real-time and get alerts if something goes wrong. This includes tracking job progress, success rates, and any errors. Good monitoring lets you react quickly to problems, which is pretty important.
Prioritize security at every step. Use strong authentication for devices and the command system. Encrypt all communications between your platform and the devices. Regularly audit your security configurations and update software to patch vulnerabilities. This protects your entire system, truly.
Consider incremental rollouts for large-scale changes. Instead of pushing a batch job to all devices at once, deploy it to smaller groups over time. This limits the potential impact of any unforeseen issues and gives you a chance to pause or revert if necessary. It's a safer approach, basically.
Make sure your devices have enough resources, like battery life, processing power, and storage, to handle the batch job. A complex update might drain a device's battery or overwhelm its processor if not planned correctly. You want to avoid breaking devices with your jobs, naturally.
Document your batch job processes and configurations. This helps future you, or other team members, understand how jobs are set up and how to troubleshoot them. Clear documentation is a pretty valuable asset for any system, honestly.
Regularly review and optimize your batch jobs. As your IoT fleet evolves or your needs change, your batch jobs might need adjustments. Keeping them efficient and relevant helps maintain system performance. This ongoing attention is, you know, pretty helpful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of using remote IoT batch jobs?
The biggest benefits include saving a lot of time by automating tasks for many devices at once. This means better efficiency and lower costs because you don't need to send people out to each device. It also helps keep all your devices consistent, making sure they all have the same settings or software, which is pretty neat.
How do remote IoT batch jobs handle devices that are offline?
When a device is offline, it just won't receive the batch job command right away. Good systems typically queue the command, meaning they'll hold onto it and try to deliver it once the device comes back online. You'll usually get a report showing which devices missed the job, so you can follow up if needed, you know, to make sure everything eventually gets done.
Is security a concern with remote IoT batch jobs?
Absolutely, security is a major concern. Because you're sending commands to many devices from a distance, it's super important to protect those commands and the devices themselves. This means using strong encryption, making sure only authorized people or systems can send commands, and regularly checking for any security weaknesses. It's a pretty big deal, honestly, to keep things safe.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Remote IoT Tasks
As more and more devices get connected to the internet, and as the idea of working from anywhere becomes even more common, remote IoT batch jobs will only grow in importance. We're seeing this trend everywhere, from remote accounting to nurses working from home, so it makes sense for physical devices too. The ability to manage vast networks of equipment efficiently and securely from a central point is, you know, a very valuable skill to have.
The future will likely bring even smarter ways to automate these tasks, perhaps with more artificial intelligence helping to predict when devices need updates or changes. This could lead to even more proactive maintenance and less manual intervention, which is pretty exciting. We might see more advanced ways to handle those tricky offline devices too, making the whole process even smoother, basically.
Keeping up with the latest in IoT technology and remote management practices will be key for anyone working with connected devices. It's a field that's always changing, so staying informed is pretty important. You can learn more about IoT device management on our site, and we also have information on how cloud platforms support remote operations that might interest you. For broader insights into the Internet of Things, you might check out resources from organizations like the IoT For All community, which is a pretty good place to start, honestly.
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remoteiot Batch Job Example Remote Aws Developing A Monitoring