Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote: Making Your Devices Work Smarter, From Anywhere
It's truly something, the way our world keeps getting more connected, isn't it? Just like how remote accounting and bookkeeping positions are steadily growing, and how folks can join remote raids in Pokémon Go from afar, the idea of managing things without being right there has really taken hold. For anyone dealing with connected gadgets, often called IoT devices, making them work together, especially when they're scattered far and wide, presents its own set of interesting challenges. You might wonder, how do we get all that information from these distant devices, process it, and then make sense of it without needing to be physically present at each location? Well, that's where the idea of a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote really starts to shine, offering a powerful way to handle huge amounts of data from afar.
Think about it: whether you're a team sharing news and tips about working remotely, or someone enjoying Xbox remote play by streaming games through the cloud without a local console, the core principle is similar. You're using distant resources to achieve a goal. For IoT, this means gathering data from sensors, machines, or smart devices located in various places—maybe across a city, a country, or even the globe. Then, you need to process this collected information in groups, or "batches," to find patterns, spot issues, or trigger actions. This kind of operation, so it's almost like a central command center for all your far-flung gadgets, is pretty vital for many modern applications.
This article aims to give you a clearer picture of how you can set up and manage these kinds of operations, especially using Amazon Web Services, or AWS. We'll explore what a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote really looks like, the tools you'll need, and a practical way to put it all together. It's about empowering you to manage your connected world efficiently, no matter how spread out your devices might be, and truly, it helps quite a bit to know these things.
Table of Contents
- The Core Idea: Remote IoT Batch Jobs with AWS
- Building Blocks for Your Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Setup
- A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Workflow
- Real-World Scenarios and Benefits of Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Overcoming Challenges in Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Deployments
The Core Idea: Remote IoT Batch Jobs with AWS
When we talk about a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote, we're really thinking about how to handle information from many devices that are not physically near us. It's a bit like managing a large, distributed team, where everyone is working from their own location. You need ways to communicate, collect their output, and process it efficiently. For IoT, this often means collecting sensor readings, operational statuses, or event logs from devices like smart meters, industrial sensors, or even connected vehicles, then processing that information in groups to get meaningful insights. This approach, you know, makes a lot of sense for efficiency.
What Are Remote IoT Batch Jobs, Anyway?
Imagine you have hundreds, or even thousands, of IoT devices spread across different buildings, farms, or even cities. Each one is constantly sending small bits of data. A "batch job" is simply a way to process a large collection of this data all at once, rather than trying to deal with each tiny piece as it arrives. Doing this "remotely" means the processing happens in the cloud, far away from the devices themselves. This is rather convenient, as it means you don't need powerful computers right where the devices are located. It's a bit like how nurses can work remotely, sharing their experiences and information from their home offices, instead of needing to be in a hospital building all the time.
For example, a batch job might collect all temperature readings from a fleet of refrigerated trucks over the past hour, then analyze them to see if any truck experienced temperatures outside a safe range. Or, it could gather energy consumption data from all smart homes in a neighborhood overnight to identify peak usage times. The key is that the processing isn't happening in real-time on the device itself, but rather on aggregated data in the cloud. This method, you see, offers a lot of flexibility.
Why AWS for Remote IoT?
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, offers a comprehensive suite of tools that are quite good for building and managing remote IoT solutions. It's like having a whole toolbox filled with specialized instruments for every task. For one thing, AWS provides services that can securely connect your devices, store their data, and then process it at scale. This means you don't have to build all that infrastructure yourself, which would be a huge undertaking. It's kind of like how you might look for remote jobs on LinkedIn or other platforms instead of building your own job board from scratch, right?
The benefits of using AWS for a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote are pretty clear. You get scalability, meaning your system can handle more devices and more data as your needs grow, without you having to worry about upgrading hardware. There's also reliability, as AWS services are designed to be highly available, so your data processing doesn't suddenly stop. And, of course, there's cost-effectiveness, because you typically only pay for the computing resources you actually use. This really helps keep things efficient, you know.
Building Blocks for Your Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Setup
To put together a successful remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote, you'll use several different AWS services, each playing a specific role. Think of it like building a DIY red dot sight: you need different parts—a CD case for the aiming dot, an LED circuit, and so on—each carefully chosen for its purpose. Similarly, in AWS, each service contributes to the overall function. This approach, it's almost like a well-oiled machine, really.
AWS IoT Core: The Remote Connection Hub
AWS IoT Core is where your remote devices first connect to the cloud. It's like the central post office for all your IoT messages. Devices can send data to IoT Core, and IoT Core can send commands back to devices. It handles the secure connection, so you don't have to worry too much about unauthorized access. It also has a "rules engine" that can take incoming data and route it to other AWS services for storage or processing. This is pretty vital for getting data from your remote devices into the cloud for batch jobs, you know.
S3: Your Remote Data Lake
Amazon S3, which stands for Simple Storage Service, is a place where you can store pretty much any kind of data. For a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote, S3 often acts as a "data lake." This means it's a central repository where all the raw, unprocessed data from your IoT devices lands. It's highly durable and scalable, so you can store vast amounts of information without much fuss. When you're ready to run a batch job, your processing service can pull the necessary data directly from S3. It's like having a huge, organized filing cabinet for all your device readings, actually.
AWS Lambda: The Serverless Workhorse
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service. What this means is you can run code without having to manage any servers. You just upload your code, and Lambda takes care of running it when needed. For remote IoT batch jobs, Lambda is often used to trigger processing when new data arrives in S3, or to perform light data transformations. It's very good for event-driven tasks, like when a new file is added to your S3 data lake, Lambda can automatically start a small processing job. This makes things really efficient, and it's quite flexible.
AWS Batch or ECS: For Heavier Lifting
While Lambda is great for quick, event-driven tasks, sometimes your batch jobs need more computing power or longer processing times. That's where AWS Batch or Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service) come in. AWS Batch lets you run thousands of computing jobs easily, so it handles the provisioning and scaling of resources for you. ECS allows you to run Docker containers, giving you more control over your computing environment. These services are ideal for complex analytics, machine learning tasks, or anything that requires significant processing power over a longer period. They really help with the bigger jobs, you know.
Amazon DynamoDB or Timestream: Data Storage for Processed Insights
After your batch job processes the raw IoT data, you'll likely want to store the results in a structured way for quick access and analysis. Amazon DynamoDB is a fast, flexible NoSQL database service that works well for storing processed IoT data, especially if you need low-latency access for dashboards or applications. For time-series data, like sensor readings over time, Amazon Timestream is specifically designed for this purpose, offering optimized storage and querying. Choosing the right database depends on how you plan to use your processed data, but either one is pretty solid for the job, in a way.
CloudWatch & SNS: Keeping Tabs on Remote Operations
Just like you'd want to keep track of your remote teams or the status of your Xbox remote play session, monitoring your remote IoT batch jobs is crucial. Amazon CloudWatch collects monitoring and operational data in the form of logs, metrics, and events. You can use it to set alarms if something goes wrong with your batch jobs or if certain data thresholds are met. Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) can then send out notifications—like emails or SMS messages—when those alarms are triggered. This helps you stay informed and quickly address any issues, even if you're not actively watching the system. It's very much about staying connected to your distant operations, you know.
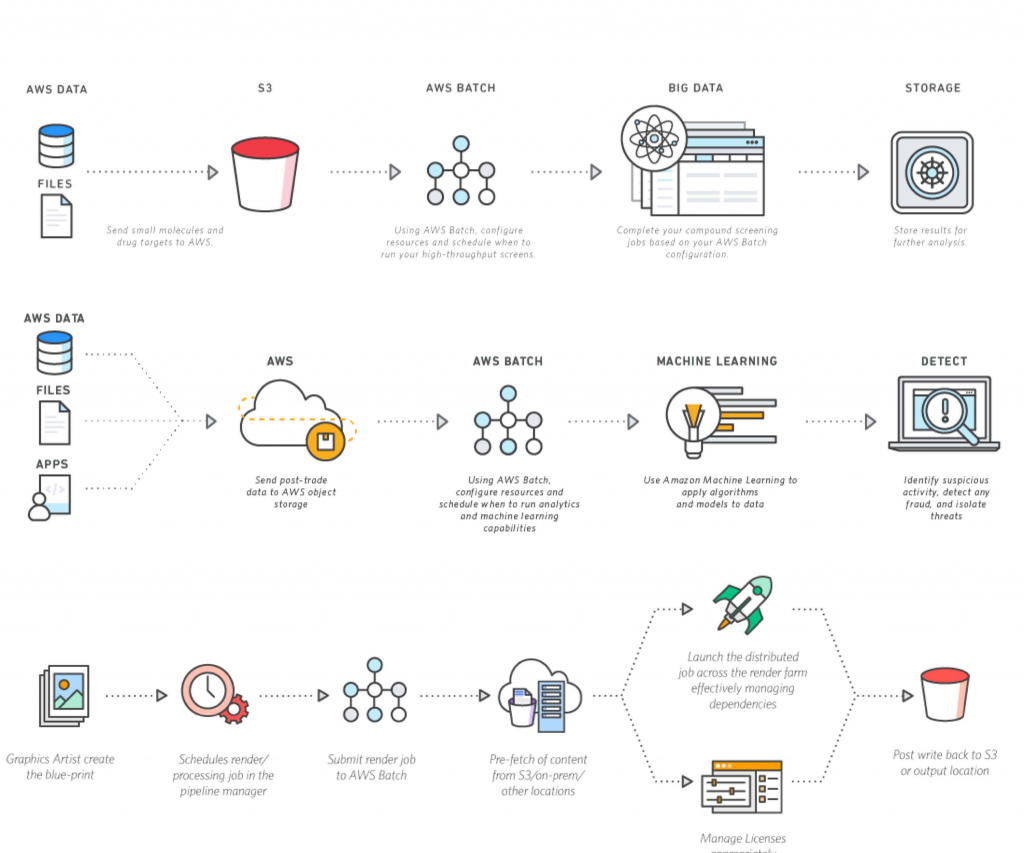
A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Workflow
Let's walk through a common flow for a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote. This will give you a better idea of how these pieces fit together to manage data from far-off devices. It's a bit like following steps to make your own optic for various shooting activities, where each step builds on the last one, right?
Step 1: Device Data Ingestion
First, your IoT devices securely send their data to AWS IoT Core. This data might be temperature readings, GPS coordinates, or equipment status updates. Within IoT Core, you'll set up a "rule." This rule tells IoT Core what to do with incoming messages that match certain criteria. For a batch job, a common rule would be to take all incoming data and send it directly to an S3 bucket. This ensures all your raw data is collected in one central, scalable location, ready for later processing. It's the initial gathering point, so to speak, for all that remote information.
Step 2: Triggering the Batch Process
Once data starts accumulating in your S3 bucket, you need a way to kick off the batch job. A very common method is to configure an S3 event notification. This means that whenever a new file (or a certain amount of new data) lands in your S3 bucket, S3 automatically sends a notification. This notification can then trigger an AWS Lambda function. The Lambda function acts as the orchestrator for your batch job. It doesn't necessarily do the heavy processing itself, but rather initiates the larger batch processing task, perhaps on AWS Batch or ECS. This setup, you know, automates the whole thing pretty well.
Step 3: Data Transformation and Analysis
Now, the Lambda function, triggered by the S3 event, can start the actual processing. If the data processing is relatively light—like simple filtering, aggregation, or reformatting—the Lambda function might handle it directly. However, for more complex tasks, like running machine learning models, performing deep statistical analysis, or processing very large datasets, Lambda would instead trigger a job on AWS Batch or ECS. These services would then pull the raw data from S3, perform the necessary transformations and analyses, and generate processed results. This part is where the real insights come from, and it's quite powerful.
Step 4: Storing Results and Taking Action
After the batch processing is complete, the processed data or derived insights need to be stored. This is typically done in a database like Amazon DynamoDB for quick access by applications or dashboards, or Amazon Timestream if the data is time-series in nature. Additionally, the batch job might trigger further actions. For instance, if the analysis reveals a critical anomaly, it could send a notification via Amazon SNS to an operations team, or even send a command back to a specific IoT device via AWS IoT Core to adjust its behavior. This final step, you see, closes the loop and makes the data actionable.
Real-World Scenarios and Benefits of Remote IoT Batch Jobs
Understanding a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote really comes to life when you see it in action. These setups are incredibly useful across many different industries, offering clear benefits. It's like finding a good way to increase your chances of getting a remote job; once you know the strategy, things just click, right?
Predictive Maintenance for Remote Assets
Consider industrial equipment spread across different factory floors or even remote mining sites. These machines generate constant data about their performance—vibration levels, temperature, pressure, and so on. A remote IoT batch job can collect all this data over time, process it to detect subtle changes that might indicate impending failure, and then alert maintenance teams. This allows for "predictive maintenance," where repairs are done *before* a breakdown occurs, saving significant costs and avoiding downtime. It's pretty much like remote accounting, where you manage finances from afar, but for machines, you know.
Fleet Management and Optimization
For companies with large fleets of vehicles—delivery trucks, buses, or even agricultural machinery—IoT devices can track location, fuel consumption, engine diagnostics, and driver behavior. A remote IoT batch job can collect this vast amount of data from all vehicles, then analyze it to optimize routes, identify inefficient driving patterns, or schedule maintenance based on actual usage rather than fixed intervals. This leads to reduced fuel costs, improved safety, and better operational efficiency across the entire fleet. It's a very practical application, really.
Smart City Data Aggregation
In smart cities, IoT sensors collect data on everything from traffic flow and air quality to waste levels in public bins. A remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote can aggregate this diverse data from thousands of sensors across a city. The batch processing can then identify traffic bottlenecks, pinpoint areas with poor air quality, or optimize waste collection routes. This helps city planners make data-driven decisions to improve urban living, making the city function more smoothly. It's quite a powerful tool for urban management, you know.
Overcoming Challenges in Remote IoT Batch Job Example Remote Remote AWS Remote Remote Deployments
While the benefits are clear, setting up a remote IoT batch job example remote remote AWS remote remote does come with its own set of things to think about. It's a bit like when you're trying to uninstall a program that just won't go away, or when you're fighting with support for months; there are sometimes tricky parts. Addressing these considerations from the start helps ensure a smoother operation. You know, it's just part of the process.
Security Considerations for Remote Devices
Connecting devices remotely means you need to pay very close attention to security. Each device should be securely authenticated to AWS IoT Core, ensuring that only authorized devices can send data. Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Implementing strong access controls, so that only necessary services and users can access the IoT data and processing resources, is also vital. It's about protecting your entire system from potential threats, much like how you'd protect your personal information when working remotely, you know.
Data Volume and Cost Management
IoT devices can generate an enormous amount of data. Managing this volume efficiently is key to keeping costs down. Using S3 lifecycle policies to move older, less frequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers, or even deleting it after a certain period, can help. Optimizing your batch processing jobs to be as efficient as possible, so they consume fewer computing resources, is also important. Monitoring your AWS costs regularly through services like AWS Cost Explorer helps you keep track of spending and identify areas for optimization. This helps ensure you're getting the most bang for your buck, really.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Remote Operations
When devices are remote and processing happens in the cloud, troubleshooting can be tricky if you don't have the right tools. Comprehensive monitoring using CloudWatch is essential to track the health and performance of your IoT devices, data ingestion, and batch processing jobs. Setting up detailed logs for your Lambda functions and batch jobs helps you diagnose issues quickly. Alerts via SNS ensure you're notified immediately of any critical problems. Having a clear understanding of your data flow and potential failure points helps you react swiftly. It's about having visibility into your distant operations, just like a distributed team needs good communication tools, you know. Learn more about remote work on our site, and link to this page AWS IoT Batch Operations for more technical details.
Frequently Asked Questions about Remote IoT Batch Jobs
Here are some common questions people often have about setting up and managing remote IoT batch jobs:
Q: How do I ensure data from my remote IoT devices is secure when it reaches AWS?
A: AWS IoT Core provides robust security features. Devices typically use X.509 certificates and TLS (Transport Layer Security) for secure, encrypted communication. You also configure IAM policies to control

Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Mastering Remote IoT Batch Job Execution In AWS