IoT Batch Job Remote: Optimizing Data Processing From Anywhere
The digital world we live in today is increasingly shaped by connected devices, and that's where the Internet of Things, or IoT, truly shines. These smart gadgets, from industrial sensors to home appliances, are constantly gathering information. They send this information to other systems and devices over the internet, making our surroundings more intelligent and responsive. This constant flow of information creates a huge amount of data, and figuring out how to handle it all effectively is a big task for many organizations, you know.
Managing all this incoming data from countless devices, especially when they are spread across wide areas, presents some interesting challenges. It's not just about collecting the data; it's also about making sense of it. Sometimes, you need to process large groups of this data all at once, rather than one piece at a time. This is where the idea of a "batch job" comes into play, and doing it from a distance, or remotely, is becoming a very important way to work.
So, considering all this, the concept of an iot batch job remote offers a powerful way to deal with these data demands. It lets businesses and individuals process big chunks of IoT data without needing to be right next to the devices themselves. This can save a lot of time and resources, and it opens up new possibilities for how we use smart technology. It's actually a pretty clever approach to a growing need, you see.
Table of Contents
- What is the Internet of Things (IoT), Anyway?
- Understanding Batch Jobs in the IoT World
- The Remote Aspect: Why Process IoT Data Off-Site?
- How IoT Batch Jobs Work Remotely: A Look at the Flow
- Key Considerations for Remote IoT Batch Processing
- Practical Tips for Setting Up Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Real-World Scenarios for IoT Batch Job Remote
- The Future of Remote IoT Data Handling
- Frequently Asked Questions about Remote IoT Batch Processing
- Final Thoughts on Optimizing Your IoT Data
What is the Internet of Things (IoT), Anyway?
The Internet of Things, often called IoT, describes devices that have sensors, processing ability, and software. These devices connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet or other communication networks. My text tells us that the IoT encompasses electronics, communication, and computer science engineering. It's really about a network of physical devices, vehicles, and appliances. They are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. This allows them to collect and share data, you know.
My text also says that the IoT refers to a network of physical devices that can transfer data to one another without human intervention. The term itself was first coined by computer scientist Kevin Ashton in 1999. It simply refers to the interconnectedness of physical devices, like appliances and vehicles. These objects have software, sensors, and connectivity which enables them to connect and exchange data. It's quite fascinating how it all works, actually.
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is a network of interrelated devices. They connect and exchange data with other IoT devices and the cloud. IoT devices typically have technology, such as sensors and software. They can include mechanical and digital machines, and even consumer objects. The term IoT refers to the collective network of connected devices and the technology that helps them talk to each other and the cloud. It also facilitates communication between the devices themselves. It’s pretty much about bringing the physical world into the digital one, you could say.
My text mentions that the IoT enables the physical world to be digitally monitored or controlled. It also states that the IoT consists of the Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). These provide the standards and rules for devices to connect to the internet and to each other. The IoT connects ordinary objects to other objects and applications in the cloud. This makes them intelligent and interactive. Such smart devices can make our lives richer and healthier, and they help to optimize the use of scarce resources. It’s a powerful idea, really.
Simply put, the term Internet of Things refers to the entire network of physical devices, tools, appliances, equipment, machinery, and other smart objects. They have the capability to collect data about the physical world. Then they transmit that data through the internet. According to Lewis, the Internet of Things, or IoT, is the integration of people, processes, and technology with connectable devices and sensors. This enables remote monitoring, status checks, manipulation, and evaluation of trends of such devices. It's a broad concept, but very practical, you see.
My text reminds us that the term was first coined by computer scientist Kevin Ashton in 1999. IoT devices are not limited to computers or machinery. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a vast array of physical objects. They are equipped with sensors and software. This enables them to interact with little human intervention. They collect and exchange data via a network. In simple terms, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the digitally connected universe of smart devices. These devices have internet connectivity, sensors, and other hardware. This allows communication and control via the web. It's all about making things smart and connected, basically.
Understanding Batch Jobs in the IoT World
When we talk about "batch jobs," we're really talking about a set of tasks that a computer system runs without much human interaction. Think of it like a list of chores that need to be done. You gather all the chores together, and then you tell the system to just go through them one by one. This is different from processing things as they happen, or in real-time. Batch jobs are great for handling large amounts of data all at once, you know.
For IoT, batch jobs are incredibly useful because IoT devices often produce a lot of data. Imagine a factory with hundreds of machines, each sending temperature readings every few minutes. Trying to process each reading as it arrives might be too much for the system to handle efficiently. Instead, you could collect all the temperature readings for an hour, or even a day, and then process them as a single "batch." This approach can save a lot of computing power and resources, so it's almost a necessity for big data volumes.
The main benefit of using batch jobs for IoT data is efficiency. When you process data in batches, you can often use computing resources more effectively. For example, you might schedule these jobs to run during off-peak hours when the network or servers are less busy. This can reduce costs and speed up the overall processing time for large datasets. It's a bit like waiting for a full load of laundry before starting the washing machine, rather than washing one shirt at a time, you could say.
Batch jobs are also good for tasks that don't need immediate results. For instance, if you're analyzing historical sensor data to spot long-term trends in equipment performance, you don't need to know the trend right this second. Running a batch job overnight to crunch all that past data works perfectly. This way, you get valuable insights without putting a constant strain on your systems. It's a practical way to get the information you need, really.
The Remote Aspect: Why Process IoT Data Off-Site?
Now, let's talk about the "remote" part of iot batch job remote. Why would you want to process IoT data away from where the devices are located? Well, there are many good reasons. One big reason is scalability. Imagine you have IoT devices spread across many different locations, perhaps in different cities or even countries. Bringing all that data to a central cloud server for processing means you don't need powerful computers at each individual site. This makes it easier to grow your operations, you know.
Cost savings are another major benefit. Setting up and maintaining powerful computing infrastructure at every location where IoT devices are deployed can be very expensive. By sending the data to a remote, centralized processing center, often in the cloud, you can use shared resources. This can be much more economical. You only pay for the computing power you use, and you don't have to worry about buying and maintaining a lot of hardware. It's a pretty smart way to manage expenses, basically.
Processing data remotely can also reduce the load on the IoT devices themselves. Many IoT devices are small and have limited processing power and battery life. Asking them to do complex data analysis on their own would drain their batteries quickly or slow them down. By collecting the raw data and sending it off for remote batch processing, the devices can focus on their primary job: sensing and transmitting. This helps them last longer and work better, you see.
Centralized management is another strong point. When all your IoT data is processed in one or a few remote locations, it's much easier to manage and monitor. You can apply consistent rules, security measures, and updates across all your data. This helps ensure that your data analysis is uniform and reliable. It also makes troubleshooting simpler. You have one place to look if something goes wrong, rather than checking many different sites, so it's a bit more organized.
Consider scenarios like remote monitoring of environmental conditions in far-flung agricultural fields. Or think about predictive maintenance for industrial machinery in isolated factories. In these cases, it's just not practical to have a full data center on site. Sending the data to a remote location for batch analysis allows you to gain insights without needing a physical presence for heavy computing. This flexibility is incredibly valuable, especially today.
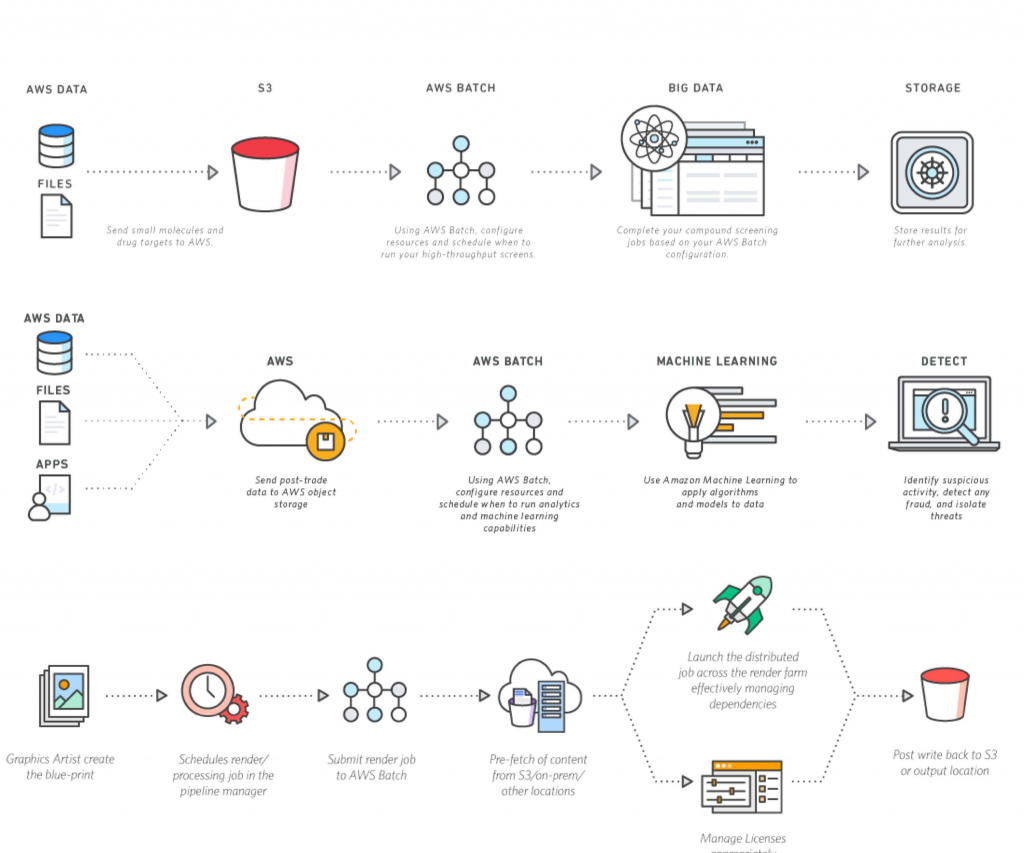
How IoT Batch Jobs Work Remotely: A Look at the Flow
So, how does an iot batch job remote actually happen? The process usually starts with the IoT devices themselves. These devices, whether they are sensors in a smart home or monitors in a factory, collect specific data. This data could be anything from temperature and humidity readings to machine performance metrics. They are constantly gathering this information, more or less.
Once the data is collected, the next step is transmission. The IoT devices send their collected data to a central location. This central spot is often a cloud platform or a dedicated edge server. The data might travel over Wi-Fi, cellular networks, or even satellite connections, depending on where the devices are located. This transfer needs to be reliable, you know, because if the data doesn't get there, it can't be processed.
After the data arrives at the remote processing location, it gets stored temporarily. This storage could be in a data lake or a database, waiting for its turn. Then, the batch processing begins. This involves running specific scripts or applications that are designed to work with large datasets. These programs clean the data, transform it, and perform the necessary analysis. For instance, they might calculate averages, identify anomalies, or generate reports. It's like sorting and analyzing a huge pile of papers all at once, basically.
The execution of these batch jobs is usually automated. They are often scheduled to run at specific times, like once a day or once a week. This scheduling ensures that the processing happens efficiently and doesn't interfere with other operations. The computing resources for these jobs are typically managed by the cloud platform. This means they can scale up or down as needed, which is very handy for varying data volumes.
Finally, after the batch job finishes its work, the results are either stored or sent back. The processed insights might be saved in a different database for later access. Or, they could be sent to dashboards, alert systems, or other applications that use the information. For example, if the batch job identifies a potential equipment failure, an alert could be sent to a maintenance team. This completes the cycle, providing actionable intelligence from raw data, you see.
Key Considerations for Remote IoT Batch Processing
When you're thinking about setting up iot batch job remote systems, there are a few important things to keep in mind. One of the biggest challenges is connectivity. IoT devices often operate in places where internet access might be unreliable or slow. Low bandwidth or high latency can cause delays in data transmission. This can affect when your batch jobs can actually start. You need a robust plan for how data will get from the device to the processing center, you know.
Security is another critical consideration. When data travels from IoT devices to a remote processing location, it's vulnerable. You need strong encryption to protect the data while it's moving. Also, you need strict access controls at the processing center to make sure only authorized people and systems can get to the data. Protecting sensitive information is paramount, especially today, so it's a very serious matter.
The sheer volume and velocity of data can also be a challenge. Some IoT deployments generate enormous amounts of data very quickly. Your remote processing system needs to be able to handle this influx without getting overwhelmed. This means choosing the right storage solutions and processing architectures that can scale to meet your needs. It's a bit like trying to catch all the raindrops in a thunderstorm; you need a big enough bucket, you could say.
Choosing the right platform is also very important. Should you use a public cloud service, or an edge computing setup? Cloud platforms offer immense scalability and managed services, which can simplify things. Edge computing, where some processing happens closer to the devices, can reduce latency and bandwidth usage for certain tasks. The choice depends on your specific needs, like how quickly you need results and how much data you're dealing with. It's a decision that can really shape your system, basically.
Data governance and compliance are also worth thinking about. Depending on the type of data you're collecting and where your devices are located, you might have specific rules about how data is stored and processed. This includes things like data residency requirements. Making sure your remote batch processing setup follows all these rules is essential to avoid legal issues. It's a detailed area, but very necessary, you see.
Practical Tips for Setting Up Remote IoT Batch Jobs
If you're looking to get started with iot batch job remote, here are some practical tips that can help. First, it's often a good idea to start small. Don't try to build a massive, complex system all at once. Begin with a pilot project, perhaps with a limited number of devices or a specific type of data. This allows you to learn and adjust without taking on too much risk. You can then expand as you gain experience, you know.
Next, automate everything you can. Manual processes for data collection, transmission, and batch job execution can be prone to errors and very time-consuming. Use tools and platforms that allow for automated data pipelines and scheduled job runs. Automation reduces the need for human intervention. This makes your system more reliable and efficient. It's a bit like setting up a self-driving car; you want it to handle the routine tasks on its own, basically.
Monitoring performance is also very important. Once your remote batch jobs are running, you need to keep an eye on them. Track how long jobs take, how much data they process, and if there are any errors. Good monitoring tools can give you insights into the health of your system. This helps you spot problems early and optimize your processes. You can't fix what you don't see, after all, so it's a very practical step.
Always plan for failures. Things can and do go wrong, whether it's a network outage, a device malfunction, or an error in your processing script. Design your system to be resilient. This means having mechanisms for retrying failed jobs, handling corrupted data, and alerting you to issues. A robust system can recover gracefully from unexpected problems. It's about being prepared for anything, you see.
Choosing the appropriate tools and technologies is also key. There are many cloud services and open-source tools available for data ingestion, storage, and batch processing. Research different options and select those that best fit your specific requirements, budget, and existing infrastructure. Don't just pick the first thing you see; take your time to find the right fit. This choice can really impact your success, you know.
Real-World Scenarios for IoT Batch Job Remote
The idea of iot batch job remote isn't just theory; it's being used in many practical ways today. Think about smart agriculture, for example. Farmers can place IoT sensors in their fields to collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Instead of analyzing this data in real-time on the farm, the sensor readings are sent to a remote cloud platform. There, a batch job can run overnight to analyze all the data from hundreds of acres. This helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization. It's a pretty efficient way to manage crops, you see.
In industrial IoT, remote batch jobs are also very valuable. Large factories or manufacturing plants have countless machines that generate operational logs and performance data. This data can be collected and sent to a remote data center. A batch job can then process these logs to identify patterns that might indicate a machine is about to fail. This allows for predictive maintenance, where repairs can be scheduled before a costly breakdown occurs. It saves money and keeps things running smoothly, basically.
Smart cities are another great example. Traffic sensors, environmental monitors, and public safety cameras all generate huge amounts of data. This data can be gathered and sent to a central cloud system. Batch jobs can then analyze traffic flow patterns over days or weeks to optimize signal timings. Or they can process air quality data to identify pollution hotspots. This helps city planners make better decisions for urban living. It's about making cities smarter and more livable, you know.
Even in healthcare, remote batch processing of IoT data finds its place. Wearable devices might collect health metrics from patients at home. This data can be securely transmitted to a remote server. A batch job could then analyze daily heart rate variability or sleep patterns for a group of patients. This helps healthcare providers spot trends or potential issues without needing constant, real-time monitoring. It's a way to provide better care from a distance, really.
These scenarios show how powerful and flexible iot batch job remote can be. By processing data away from the source, organizations can gain valuable insights from their IoT deployments. This happens without needing complex infrastructure at every single location. It opens up many possibilities for efficiency and innovation, you could say.
The Future of Remote IoT Data Handling
Looking ahead, the role of iot batch job remote is likely to grow even more. We're seeing a trend towards more intelligence moving closer to the "edge," meaning closer to the IoT devices themselves. While some data will still be sent for remote batch processing, more initial filtering and basic analysis might happen on the device or a local gateway. This can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, which is very helpful, you know.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will also become more common in remote batch jobs. Instead of just running predefined analyses, these jobs will be able to learn from the data. They will identify more complex patterns and make predictions. Imagine a batch job that not only flags potential equipment failures but also suggests the most likely cause. This makes the insights much more actionable, basically.
Increased automation will also be a big part of the future. The entire lifecycle of IoT data, from collection to processing and even acting on insights, will become more automated. This means less human intervention will be needed. Systems will be able to adjust and optimize themselves. This will lead to even greater efficiency and reliability in handling large volumes of IoT data. It's about making things smarter and more self-sufficient, you see.
We can also expect to see more specialized platforms and tools designed specifically for remote IoT data processing. These tools will make it easier for businesses to set up and manage their batch jobs. They will handle the complexities of data ingestion, storage, and analysis. This will lower the barrier to entry for many organizations. It's about making powerful technology more accessible, you know.
The ongoing growth of IoT devices means an ever-increasing amount of data. Remote batch processing offers a scalable and cost-effective way to manage this data flood. As technology advances, these systems will become even more capable and intelligent. This will unlock new opportunities for innovation across many industries. The future looks quite promising for this area, really.
Frequently Asked Questions about Remote IoT Batch Processing
What is the main advantage of using remote batch jobs for IoT data?
The biggest advantage is handling large amounts of data efficiently and cost-effectively. It lets you process information from many devices without needing powerful computers at each location. This helps you save money and scale your operations easily, you know.
Is remote IoT data processing secure?
It can be very secure, but it needs careful planning. You must use strong encryption for data as it travels. Also, you need strict access controls where the data is processed. Making security a top priority is very important, you see.
Can I process IoT data in real-time instead of using batch jobs?
Yes, you can process IoT data in real-time for immediate needs. Batch jobs are for when you need to analyze large historical datasets or when immediate results aren't necessary. Often, a combination of both real-time and batch processing is used, depending on the specific task. It's about choosing the right tool for the job, basically.
Final Thoughts on Optimizing Your IoT Data
Thinking about how much data IoT devices generate, finding good ways to process it is really important. The idea of an iot batch job remote offers a very practical solution for many situations. It allows organizations to collect vast amounts of information from devices spread out everywhere. Then, they can send this information to a central location for efficient analysis. This approach can lead to big savings and better insights, you know.
By using remote batch processing, businesses can unlock the full value of their IoT investments. They can make smarter decisions, improve operations, and create new services. It’s about taking raw data and turning it into something truly useful. Considering the growth of connected devices, mastering this kind of data handling is a valuable skill for anyone working with IoT, you see.

Remote IoT Batch Job Example: Revolutionizing Automation With AWS
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Mastering Remote IoT Batch Job Execution In AWS