Understanding A Remote IoT Batch Job Example For Better Operations
The way we work, and indeed, how our technology operates, has truly changed a lot lately, hasn't it? Many folks are finding themselves working from home, and even things like managing far-off devices are becoming a normal part of our day. It's a bit like how remote accounting jobs are popping up everywhere, or how you can join remote raids in Pokémon Go – the idea of doing things from a distance is just getting bigger. This shift means we're always looking for smart ways to handle tasks, especially when we're dealing with lots of data from devices that aren't right next to us.
Think about it: whether it's a team sharing tips on working from anywhere, or someone figuring out how to stream Xbox games without owning a console, the core idea is about getting things done effectively, even when you're not physically there. For businesses with many connected gadgets, this means finding good methods to collect and process information without needing to visit each one. That's where a really neat idea comes into play: handling groups of tasks for those far-off devices all at once.
This kind of work, a remote IoT batch job example, is becoming quite important for companies that want to make good choices based on what their devices are telling them. It's about gathering up all that information, tidying it up, and then doing something useful with it, all without someone needing to be on-site. It's a way, you know, to get a lot done efficiently, which is pretty handy in our busy world.
Table of Contents
- What Are Remote IoT Batch Jobs?
- A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example
- Setting Up Your Own Remote IoT Batch System
- Common Challenges and How to Handle Them
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
What Are Remote IoT Batch Jobs?
So, what are we really talking about when we say "remote IoT batch job example"? Well, it's pretty much what it sounds like. Imagine you have a bunch of smart devices out in the world, perhaps in different buildings or even across a country. These devices are constantly gathering information – maybe temperature readings, machine performance data, or even how many times a door opens. A "batch job" means you're not processing this information one tiny piece at a time, as it arrives. Instead, you wait until you have a good chunk of it, or until a certain time, and then you process that whole group together.
The "remote" part simply means you're doing all this processing from a different spot than where the devices are located. You're not physically there with the sensors; you're likely sitting at a computer, perhaps in an office or at home, managing the data flow and the processing tasks through a network. This kind of setup, you know, is really helpful for many kinds of operations.
It's a bit like how some nurses now work from home, looking at patient data and making decisions without being in the hospital itself. The core idea is that the work happens somewhere else, away from the physical source. For IoT, this could mean analyzing data from smart city sensors from a central office, or checking on industrial machinery in a factory from miles away. It's a rather efficient way to handle things, actually.
Why Batch Processing Makes Sense
You might wonder, why not just process data as soon as it comes in? That's called real-time processing, and it's great for some things, like immediate alerts if a machine is about to break. But for many other tasks, batch processing just makes more sense. For one thing, it can be much more cost-effective. Processing data continuously can use a lot of computing resources, which can get pricey.
When you collect data in batches, you can schedule the processing for times when computing resources are cheaper or when your systems aren't as busy. It's also often easier to handle large volumes of data this way. Imagine trying to sort a million tiny pebbles one by one versus scooping them up in big buckets and sorting them in batches. The bucket method, you know, is usually faster for big piles.
Batch processing also lets you do more complex analysis. You can look at trends over hours, days, or weeks, which is hard to do if you're only ever looking at one tiny piece of data at a time. This approach, you see, helps you get a bigger picture from all that information.
The "Remote" Angle: How It Fits
The "remote" aspect of these jobs is pretty important, especially today. Many companies have devices spread out over a wide area, or even globally. It's just not practical to have someone physically present at every location to manage the data. This is where the remote part truly shines.
By setting up a remote IoT batch job example, you can have a central team or even automated systems that pull data from all those far-off devices. They then process it, and deliver insights, all from a single location. This is very much like how remote data entry or admin assistant jobs let people work from home, connecting to company systems over the internet. It's about access and control, no matter where you are.
This setup also makes it easier to scale your operations. If you add more devices, you don't necessarily need more people on the ground. Your remote processing system can simply handle the increased data load. It's a way, you know, to grow your business without needing to expand your physical footprint everywhere.
A Practical Remote IoT Batch Job Example
Let's walk through a real-world kind of remote IoT batch job example. This will help make the whole idea a lot clearer. We'll look at a situation where a company uses this approach to make better decisions.
The Scenario: A Smart Farm
Imagine a large agricultural company that manages several farms spread across different regions. Each farm has hundreds of IoT sensors planted in the soil. These sensors measure things like soil moisture, temperature, nutrient levels, and even sunlight exposure. The goal is to optimize crop growth, use water efficiently, and predict potential issues like disease outbreaks.
It would be very difficult, almost impossible, for someone to visit each farm daily to collect data from every sensor. Plus, trying to make sense of all that raw data on the spot would be a huge task. This is where a remote IoT batch job becomes incredibly useful, you see.
The company needs to gather all this information, process it, and then give advice to the farm managers. They want to know, for instance, which fields need watering, or if a specific crop variety is thriving in certain soil conditions.
The Data Flow: From Soil to Server
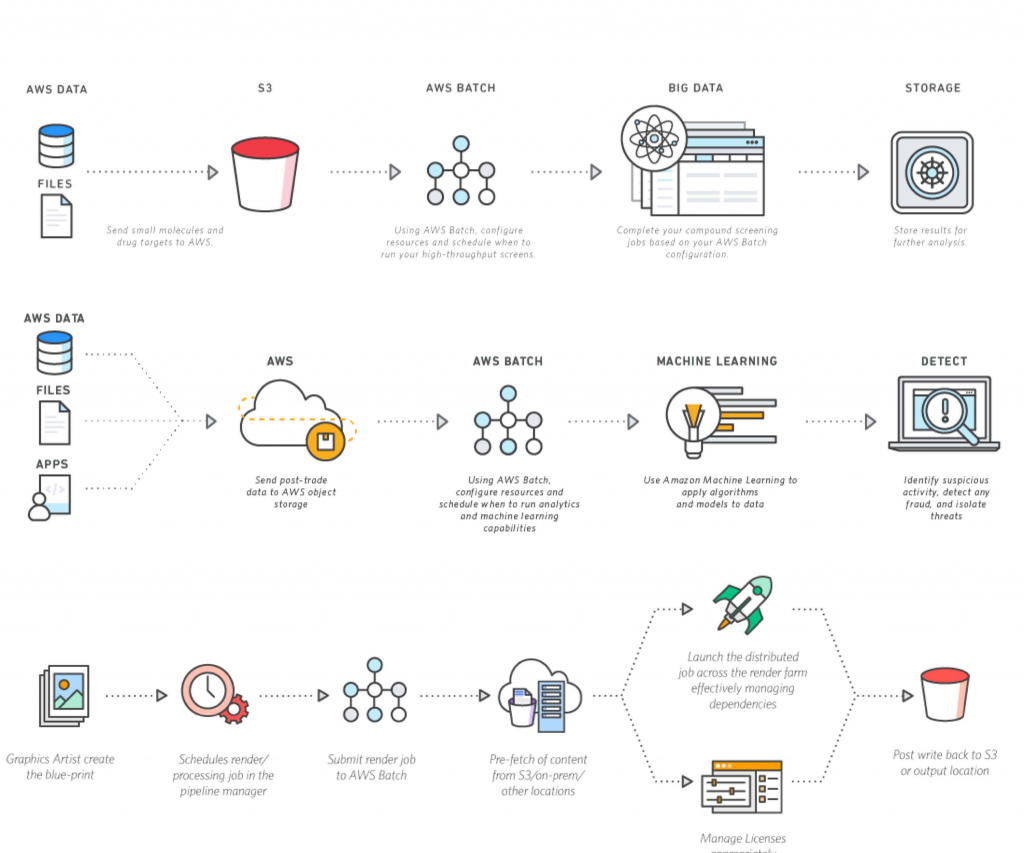
Here's how the data travels in our remote IoT batch job example. The sensors in the fields collect readings throughout the day. Instead of sending every single reading immediately, they might store them locally for a few hours, or even a full day. Then, at a set time, perhaps late at night when network traffic is low, each sensor or a local gateway device on the farm sends its collected batch of data over the internet to a central cloud server.
This data, you know, arrives at the cloud server and is put into a special storage area, like a big digital warehouse. It's not processed right away. It just waits there with all the other data coming in from the different farms. This waiting period is a key part of the "batch" idea.
This method means the sensors don't need to be constantly connected, which saves battery life and reduces network strain. It's a very practical way to gather information from far-off places.
Processing Steps: Making Sense of It All
Once all the data batches from every farm have arrived in the cloud storage, the remote batch job kicks in. This job is typically a set of automated programs running on powerful cloud computers. First, it pulls all the new data from the storage. Then, it starts cleaning it up. This might involve removing duplicate readings, fixing errors, or converting different units of measurement so everything is consistent.
Next, the job performs various analyses. It might calculate average soil moisture levels for each field, compare current temperatures to historical data, or look for unusual patterns that could suggest a pest problem. It might also combine sensor data with other information, like weather forecasts or satellite imagery, to get a fuller picture. This is where the true value, you know, starts to show.
Finally, after all the calculations and analyses are done, the batch job stores the results in a database. It might also generate reports, charts, or even send automated alerts to farm managers. All of this happens without anyone needing to be physically present at the farms or directly running the programs. It's all done remotely, automatically, and in batches.
Benefits Realized: Growing Smarter
This remote IoT batch job example offers many good things for the agricultural company. For one, it significantly reduces operational costs. They don't need staff constantly monitoring sensors or traveling between farms just to collect data. The process is automated and runs efficiently.
Secondly, it leads to much better decision-making. Farm managers receive daily, consolidated reports with actionable insights, rather than just raw numbers. They can see which fields are dry and need watering, or which areas might be prone to disease, allowing them to respond quickly and precisely. This kind of information, you know, is golden for farming.
It also helps with resource optimization, like using less water or fertilizer because they know exactly where and when it's needed. This makes the farming operations more sustainable and profitable. The ability to manage so much data from afar, you see, really changes how they do business.
Setting Up Your Own Remote IoT Batch System
Thinking about setting up your own remote IoT batch job example? It's a very achievable goal, but it does involve a few key steps and considerations. Just like finding remote jobs, it's about knowing where to look and how to prepare.
Choosing the Right Tech Pieces
First, you'll need to pick the right technology for your devices. This means sensors that can collect the data you need and, importantly, can store it temporarily before sending it in a batch. You'll also need a way for these devices to connect to the internet, perhaps through a local gateway or directly if they have cellular or Wi-Fi capabilities.
For the remote processing part, cloud platforms are usually the best choice. Services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud offer all the tools you'll need: secure storage for your incoming data, computing services to run your batch jobs, and databases to store the processed results. They also provide ways to schedule your jobs, so they run automatically at specific times. This gives you, you know, a lot of flexibility.
You might also want to look into specific tools for data processing. There are many open-source options and commercial software that can help you clean, transform, and analyze your data effectively. It's about finding the right fit for your particular needs.
Ensuring Security: Keeping Things Safe
Security is a big deal when you're dealing with remote IoT devices and data. You need to make sure that the data collected from your devices is sent securely to your cloud storage. This often involves using encryption, which scrambles the data so only authorized systems can read it. Think of it like putting your data in a locked box before sending it through the mail.
You also need to protect your cloud systems from unauthorized access. This means strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and carefully managing who has permission to access your data and run your batch jobs. It's a bit like how a subreddit about remote work has rules to keep things orderly and safe; your data systems need rules too. Keeping things safe, you know, is paramount.
Regularly updating your device software and cloud configurations is also a must. New threats appear all the time, so staying current helps keep your system protected.
Managing Scale: Growing With Your Needs
As your operation grows and you add more devices, your remote IoT batch job example needs to be able to handle more data. This is where the scalability of cloud platforms really helps. You can easily increase the computing power and storage space as needed, without having to buy new physical equipment.
Designing your batch jobs to be efficient is also important. This means writing code that can process large amounts of data quickly and making sure your storage solutions can keep up with the incoming volume. It's like building a road that can handle more cars as traffic increases. Planning for growth, you see, will save you headaches later.
Testing your system with larger and larger amounts of data is a good practice. This helps you find any bottlenecks or issues before they become real problems when your system is fully operational. It's a rather smart way to prepare for the future.
Common Challenges and How to Handle Them
Even with the best planning, setting up a remote IoT batch job example can have its tricky spots. It's a bit like dealing with software that just won't uninstall, as some folks in the "My text" shared; sometimes, things just don't work as expected. Knowing what challenges might pop up helps you get ready for them.
Connectivity Issues: When the Signal Drops
One of the most common issues with remote devices is unreliable internet connection. Devices might be in areas with spotty Wi-Fi or cellular service. If a device can't send its batch of data when scheduled, that information could be lost or delayed.
To handle this, devices should be designed to store data for longer periods if needed and try to resend it later. Implementing a robust "retry" mechanism is important, where the device keeps trying to send the data until it succeeds. Also, having local data processing capabilities on the device itself, even if basic, can help ensure critical information is still acted upon, even without a constant connection.
Data Volume: A Flood of Information
As you add more devices, the sheer amount of data they generate can become overwhelming. This isn't just about storage; it's also about how long it takes to process all that information. If your batch jobs take too long to run, your insights might not be timely enough.
To manage this, consider strategies like data compression at the device level before sending, which reduces the size of the data. Also, optimizing your batch processing code and using more powerful cloud computing resources can speed things up. Sometimes, you might also need to decide what data is truly essential and only send or process that.
Device Management: Keeping Track
Keeping track of hundreds or thousands of remote IoT devices can be a challenge. How do you know if a device is offline, or if its battery is low, or if its software needs an update? It's hard to manage things when you can't just walk over and check.
Implementing a device management platform is really helpful here. These platforms let you monitor device health, send commands to devices (like telling them to update their software), and even troubleshoot issues remotely. They give you a central view of all your distributed devices, making remote management much more practical. You can learn more about Google Cloud IoT Core, for instance, which is a platform for connecting, managing, and ingesting data from devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
People often have questions about how these remote systems work. Here are a few common ones.
What exactly is a remote IoT batch job? It's a process where smart devices, located far away, collect data over a period of time and then send that data in groups (batches) to a central system, usually in the cloud. This central system then processes all that collected data at once, rather than piece by piece, to get useful information.
Why would I use batch processing for remote IoT devices? Using batch processing can save you money on computing resources because you can schedule processing during off-peak times. It also helps manage large amounts of data more efficiently and allows for more complex analysis over longer periods, giving you a bigger picture of what's happening.
What tools help with remote IoT batch processing? Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud are key, as they provide storage, computing power, and scheduling services. You'll also use programming languages like Python or Java for writing your batch jobs, and databases for storing your processed insights. Specific IoT platforms from these cloud providers also help manage the devices themselves.
Final Thoughts
The world of remote operations is just getting bigger, and understanding a good remote IoT batch job example can open up many new possibilities for businesses. It's about taking all that information from your far-off devices and turning it into something truly valuable, all without needing to be right there. This approach, you know, makes a lot of sense for today's way of doing things.
It lets companies be more flexible, save resources, and make smarter choices, no matter where their devices are located. It's a powerful way to use technology to your advantage, very much like how remote teams share their experiences to improve how everyone works. We are always learning more about remote work solutions on our site, and you can also find out about how to manage your IoT devices effectively.
Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remote IoT Batch Jobs On AWS: Examples & Best Practices

Remoteiot Batch Job Example Remote Aws Developing A Monitoring