Getting Your Remoteiot Device Ssh Tutorial Started: A Simple Guide For Connecting Safely Today
Do you have a smart device, perhaps a tiny computer like a Raspberry Pi, sitting somewhere in your home or office, and you wish you could talk to it without being right next to it? Many people feel this way, you know. It's a common thought for anyone with these little gadgets. You might want to check on things, make changes, or just see what your device is up to, even when you are far away. This idea of reaching out to your devices from a distance is pretty appealing for many reasons.
This guide is all about how you can do just that using something called SSH. SSH, or Secure Shell, helps you get a safe way to connect to your remote IoT device. It is almost like having a direct line to your device, no matter where you are. This method is very popular for keeping an eye on things, sending commands, or fixing little problems with your smart gadgets.
We will walk through the steps, making sure everything is clear and easy to follow. You will learn what you need to begin, how to set up your device, and how to make that first connection. We will also talk about keeping your connection safe, which is a big part of this whole process. So, let's get ready to make your IoT devices truly remote.
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why Use It for IoT?
- Things You Need Before You Begin
- Setting Up Your IoT Device for SSH
- Connecting to Your IoT Device with SSH
- Making Your SSH Connection Safer
- Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
- What Else Can You Do with Remote IoT Access?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is SSH truly safe for my IoT devices?
Yes, it is, provided you set it up correctly. SSH uses strong encryption, which keeps your connection private. It also lets you use special keys instead of just passwords, making it even harder for unwanted people to get in. So, with a bit of care, it's very safe, actually.
What kind of IoT devices can I use SSH with?
You can use SSH with many kinds of devices. Any device that runs a version of Linux, like a Raspberry Pi or an ESP32 with a specific firmware, often supports SSH. It's usually for devices that have a proper operating system. Smaller, simpler sensors might not have this ability. You know, it really depends on the device itself.
What if I cannot connect to my device using SSH?
There are a few common reasons this happens. It could be a wrong IP address, a firewall blocking the connection, or even the SSH service not running on your device. We will go over some ways to check these things in this guide. Sometimes, it's just a simple setting that needs a little tweak, you see.
What is SSH and Why Use It for IoT?
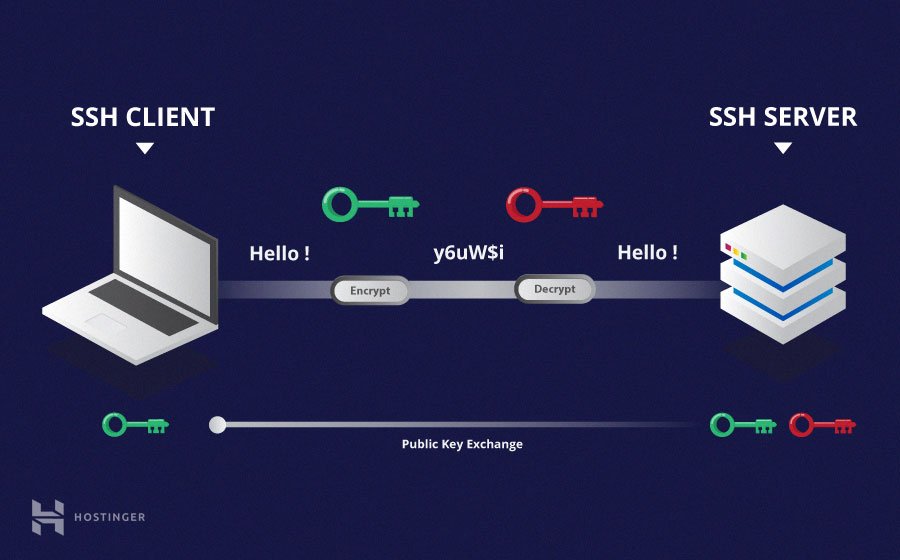
SSH stands for Secure Shell. It is a way to get into another computer over a network, and it does this in a very safe way. Think of it as a secret tunnel for your commands and data. When you use SSH, you are essentially getting a text-based window into your remote device. This lets you type commands as if you were sitting right in front of it. This is really useful for IoT devices, as they often don't have a screen or keyboard. So, this tool becomes quite important.
A Little About Secure Connections
The "secure" part of SSH is a big deal. It means that everything you send and receive through this connection is scrambled. This scrambling, or encryption, keeps your information private. No one else on your network can easily snoop on what you are doing or what your device is telling you. This protection is very important, especially when your device might be in your home or connected to the internet. It gives you peace of mind, you know.
Without SSH, if you were to connect to your IoT device, your information might be sent in plain text. This is like sending a postcard where everyone can read it. With SSH, it's more like sending a sealed letter. This makes it a much better choice for managing any kind of smart device. It’s a good step for anyone looking to keep their home network safe.
Why Remote Access Helps
Having remote access to your IoT devices is a huge benefit. Imagine you have a sensor in your garden or a smart light in a hard-to-reach spot. If something goes wrong, or if you just want to change how it works, you don't have to go physically to the device. You can just connect from your computer, wherever you are. This saves a lot of time and effort, obviously.
For people who have many devices, or devices spread out, remote access becomes almost a necessity. You can check on all of them from one spot. You can update their software, fix problems, or gather data without moving from your chair. This makes managing your smart home or smart garden much, much easier. It's a very practical solution for modern living, really.
Things You Need Before You Begin
Before you start connecting to your IoT device with SSH, you need to gather a few things. Having these ready will make the whole process go much smoother. It's like preparing your ingredients before you start cooking. This little bit of preparation saves you from stopping halfway through. So, let's look at what you will want to have on hand.
Your IoT Device
First, you need the IoT device itself. This could be a Raspberry Pi, an Orange Pi, or another similar small computer. Make sure it is powered on and connected to your network. It needs to be able to talk to other devices on your home or office network. Usually, this means it is connected to your Wi-Fi or directly plugged into your router with an Ethernet cable.
Also, your device needs to have an operating system installed that supports SSH. Most Linux-based systems, like Raspberry Pi OS, come with SSH built-in or can have it added easily. Make sure your device is set up and running before you try to connect. You know, a working device is a good start.
A Computer to Connect From
You will need another computer to connect from. This is usually your laptop or desktop computer. It can be a Windows PC, a Mac, or a Linux machine. This computer will be where you type your SSH commands. It is your control center for your remote IoT device.
For Windows users, you might need to install a special program called PuTTY, or use the built-in OpenSSH client that newer Windows versions have. Mac and Linux users usually have SSH tools already on their systems. We will cover how to use these in the next sections. It's pretty straightforward, actually.
Network Setup Thoughts
Both your IoT device and the computer you are connecting from need to be on the same network, at least for the first connection. This usually means they are both connected to the same Wi-Fi router. If you want to connect from outside your home network, that is a bit more advanced and involves setting up port forwarding on your router. We will focus on connecting within your local network for this tutorial, as a matter of fact.
Knowing your IoT device's IP address is also very important. This is like its phone number on your network. You will use this address to tell your computer where to connect. We will show you how to find this address soon. Having a stable network connection for both devices is key for success.
Setting Up Your IoT Device for SSH
Now that you have your tools ready, it is time to prepare your IoT device for SSH connections. This usually involves a few simple steps to make sure the SSH service is running and ready to accept connections. The process can vary a little depending on your specific device and its operating system, but the general idea is the same.
First Steps on the Device
If your IoT device is new, you might need to connect a screen and keyboard to it for the very first setup. This is just to get it online and ready. For a Raspberry Pi, for example, you would install Raspberry Pi OS onto an SD card, put it in the Pi, and boot it up. Then you would connect it to your Wi-Fi or wired network.
Make sure you know the default username and password for your device. For Raspberry Pi OS, the default username is often `pi`, and the password is `raspberry`. You will need these details to log in remotely. It is a good idea to write these down somewhere safe for now.
Enabling SSH
Many operating systems for IoT devices have SSH turned off by default for security reasons. You will need to turn it on. For Raspberry Pi OS, there are a few ways to do this.
One easy way is to use the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool. You can find this in the main menu under Preferences. Go to the 'Interfaces' tab and make sure 'SSH' is set to 'Enabled'. Then click 'OK'.
Another way, if you are comfortable with the command line, is to type `sudo raspi-config` in a terminal window. From there, go to 'Interface Options', then 'SSH', and choose to enable it. After that, you might need to restart your device for the changes to take effect. This is a common step, you know.
Finding Your Device's Address
To connect to your device, you need its IP address. This is a series of numbers that identifies it on your network, like `192.168.1.100`.
On your IoT device, if you have a screen connected, you can open a terminal and type `hostname -I` (that's a capital 'i'). This command will usually show you the device's IP address.
If you do not have a screen, you might be able to find it from your router's administration page. Log into your router (usually by typing its IP address, like `192.168.1.1` or `192.168.0.1`, into a web browser). Look for a section that lists connected devices or a DHCP client list. Your IoT device should appear there with its name and IP address. This is a very common way to find it, actually.
Connecting to Your IoT Device with SSH
Once your IoT device is ready, you can make your first SSH connection from your computer. The steps vary a little depending on whether you are using Windows, Mac, or Linux, but the core idea is the same. You will tell your computer to open a secure connection to your device's IP address using its username.
From a Windows Computer
For Windows, you have a couple of choices.
Many people use a program called PuTTY. You can download it from its official website. Once installed, open PuTTY. In the 'Host Name (or IP address)' box, type your device's IP address. Make sure the 'Port' is set to 22 (this is the standard SSH port). Choose 'SSH' as the connection type. Then click 'Open'.
If you have a newer version of Windows (Windows 10 or 11), you might have OpenSSH client built in. You can open the 'Command Prompt' or 'PowerShell'. Then type `ssh username@ip_address` (replace `username` with your device's username, like `pi`, and `ip_address` with your device's IP address). Press Enter. This is often simpler, you know.
From a Mac or Linux Computer
Mac and Linux systems usually have the SSH client already installed. This makes connecting very simple.
Open a 'Terminal' window. You can usually find this in your Applications folder (on Mac, look in Utilities) or by searching for 'Terminal'.
In the terminal, type `ssh username@ip_address` (again, replace `username` and `ip_address` with your device's details). Press Enter. It's a very direct way to get connected, really.
Your First Connection
The very first time you connect to a device using SSH, your computer might ask you to confirm the connection. It will show you a message about the host's authenticity and ask if you want to continue. Type `yes` and press Enter. This adds the device's unique identifier to your computer, so it knows it is connecting to the right place next time.
After that, you will be asked for the password for the username you provided. Type the password carefully (it usually won't show characters as you type, which is normal for security). Press Enter. If everything is correct, you will see a command prompt for your remote IoT device. You are in! You can now type commands directly to your device. This is a pretty cool moment, too.
Making Your SSH Connection Safer
Connecting to your IoT device remotely is great, but keeping that connection safe is even better. There are a few very important steps you should take to make sure only you can access your device. These steps help prevent unwanted access and keep your smart gadgets secure. So, let's look at how to make your SSH connection much more robust.
Changing Default Passwords
The first and most important step is to change any default passwords on your device. For example, if your Raspberry Pi uses the default `pi` username and `raspberry` password, change it right away. These default passwords are widely known and can be a big security risk.
To change the password on your IoT device (after you have connected via SSH), type `passwd` and press Enter. It will ask you for your current password, then for a new one, and then to type the new one again to confirm. Choose a strong password: one that is long, with a mix of letters (upper and lower case), numbers, and special characters. Do not use easy-to-guess things like your birthday or pet's name. This is a basic but very powerful step.
Using SSH Keys for Better Security
SSH keys offer a much stronger way to log in than passwords alone. An SSH key pair has two parts: a private key (which you keep secret on your computer) and a public key (which you put on your IoT device). When you try to connect, your computer uses your private key to prove who you are to the device.
To set this up, you first generate a key pair on your computer. On Mac or Linux, you can type `ssh-keygen` in your terminal. For Windows, PuTTY comes with a tool called PuTTYgen. Follow the steps to create your keys.
Once you have your public key, you need to copy it to your IoT device. The public key goes into a file called `authorized_keys` inside a hidden folder named `.ssh` in your user's home directory on the device. There are tools like `ssh-copy-id` (on Linux/Mac) or manual methods to do this. This method is very secure, and many people prefer it.
Disabling Password Access
After you have successfully set up SSH key access and confirmed it works, you can make your device even safer by turning off password login entirely. This means that only someone with your private SSH key can log in. This is a big step up in security.
To do this, you need to edit the SSH server configuration file on your IoT device. Connect via SSH, then type `sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config` to open the file. Look for a line that says `PasswordAuthentication yes`. Change `yes` to `no`. Also, make sure `PubkeyAuthentication` is set to `yes`.
Save the file (Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter in nano) and restart the SSH service by typing `sudo systemctl restart ssh`. Now, only your SSH key will work for logging in. This is a much safer setup, and it's almost always recommended for devices that are exposed to the internet.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Sometimes, things do not go as planned, and you might have trouble connecting to your IoT device. Don't worry, this happens to everyone. Most connection problems have simple fixes. We will go through some common issues and how to check them. A little patience goes a long way here, you know.
Device Not Found
If you get a message like "Host unreachable" or "Connection timed out," it often means your computer cannot find your IoT device on the network.
First, double-check the IP address you are using. Is it correct? Has your device's IP address changed? Sometimes routers assign new IP addresses.
Second, make sure your IoT device is powered on and connected to the network. Is its Wi-Fi light on? Is the Ethernet cable plugged in properly?
You can also try to 'ping' your device from your computer. Open a terminal or command prompt and type `ping ip_address` (replace `ip_address` with your device's IP). If you see replies, the device is on the network. If not, there is a network connection problem.
Connection Refused
A "Connection refused" message usually means your computer found the device, but the device would not let the SSH connection happen.
This often means the SSH service is not running on your IoT device. Go back to your device (if you can, with a screen and keyboard) and make sure SSH is enabled and the service is running. On Linux-based systems, you can type `sudo systemctl status ssh` to check its status. If it's not running, try `sudo systemctl start ssh`.
It could also be a firewall on your IoT device blocking the connection. If you have set up a firewall, make sure it allows connections on port 22. This is a common issue, actually.
Authentication Problems
If you get "Permission denied" or "Authentication failed," it means your computer connected to the device, but you could not log in.
Double-check the username and password you are using. Are they correct? Remember, passwords are case-sensitive.
If you are using SSH keys, make sure your private key is correct and that the public key is properly installed on your IoT device in the `authorized_keys` file. Also, check the permissions of your `.ssh` folder and the `authorized_keys` file on the device. They need to be set correctly for SSH to work. This is a bit more involved, but it is a common reason for this message.
What Else Can You Do with Remote IoT Access?
Once you have a working SSH connection to your remote IoT device, a whole world of possibilities opens up. You are no longer tied to being physically near your device. This remote access is not just for setting things up; it is for ongoing management and control. So, what kinds of things can you accomplish with this newfound freedom?
Checking Device Health
You can use SSH to check how your IoT device is doing. Is it running out of storage space? Is its processor working too hard? Is it getting too hot? You can run commands like `df -h` to see disk usage, `top` or `htop` to check processor and memory use, and `vcgencmd measure_temp` (on a Raspberry Pi) to see its temperature. This helps you keep your device running smoothly and catch problems early. It's like a remote check-up, you know.
Updating Software
Keeping your device's software up-to-date is very important for security and performance. With SSH, you can easily do this from anywhere. For Linux-based devices, you can typically run commands like `sudo apt update` and `sudo apt upgrade` to get the latest software and

How To Access And Control Your Devices From Anywhere Using Ssh Remote
How To Access Your IoT Device Remotely: The Ultimate SSH Tutorial
Comprehensive RemoteIoT Web SSH Tutorial For Secure Access